~ak~
- 4
- 0
Homework Statement
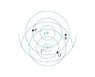
The figure shows the circular wave fronts emitted by two wave sources.
Make a table with rows labeled P, Q, and R and columns labeled r1, r2, \Deltar, and C/D. Fill in the table for points P, Q, and R, giving the distances as multiples of \lambda and indicating, with a C or a D, whether the interference at that point is constructive or destructive
Homework Equations
no real formula, given, just count the rings in the wave front pattern
The Attempt at a Solution
so i got mostly everything except r2 for P and R...im thinking it should be 7/2\lambda for both, but apparently its not...what am i doing wrong?