buildingblocs
- 17
- 1
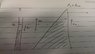
I am trying to establish a mathematical relationship between heights h1 and h2 (please refer to figure attached) for a manometer whose RHS channel is the shape of a triangle (defined by a base length and the angle theta). I want to be able to calculate the heights h1 and h2 for a given change to the pressure p1. Any help or a point in the right direction would be much appreciated.
Regards,
ps. This is not an practice question, I am hoping to do this with multiple manometer with various geometries.
Regards,
ps. This is not an practice question, I am hoping to do this with multiple manometer with various geometries.