- #1
Mikkel
- 27
- 1
Hello!
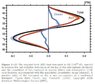
I'm currently studying meridional heat transfer, but I'm struggeling to understand the attached figure.
I don't understand why the ocean contributes more than the atmosphere near the equator and why it suddenly falls off towards the mid-latitudes. Also, why the atmosphere peaks at around 40 degress.
All in all, I don't understand why the shapes are the way they are.
I'm currently studying meridional heat transfer, but I'm struggeling to understand the attached figure.
I don't understand why the ocean contributes more than the atmosphere near the equator and why it suddenly falls off towards the mid-latitudes. Also, why the atmosphere peaks at around 40 degress.
All in all, I don't understand why the shapes are the way they are.