- #1
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
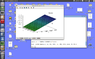
Why Do Different Software Show Varied Results for 3D Damped Spring Plots?
In summary, damping in spring plots refers to the resistance of a system to oscillate or vibrate. It can be calculated using a formula that takes into account the amplitude and time intervals of the oscillations. The logarithmic scale on the x-axis is used to better visualize the decrease in amplitude over time. Damping affects the resonance frequency by decreasing it, and this has various real-life applications in fields such as automotive technology, music, and structural engineering.
1. What is the significance of damping in spring plots?
Damping in spring plots refers to the resistance of a system to oscillate or vibrate. It is an important factor in determining the behavior of a system, as it affects the amplitude and frequency of the oscillations. In damped spring plots, damping is represented by a coefficient which determines the rate at which the oscillations decrease.
2. How do you calculate the damping coefficient in a spring plot?
The damping coefficient can be calculated by measuring the amplitude of the oscillations at different time intervals and using the formula: b = (1/2pi) * ln(Ai/Ai+1), where b is the damping coefficient, A is the amplitude, and i is the time interval.
3. Why do damped spring plots have a logarithmic scale on the x-axis?
The logarithmic scale on the x-axis is used to better visualize the decrease in amplitude over time. Since the damping coefficient is calculated using the logarithmic function, plotting the data on a logarithmic scale results in a straight line, making it easier to analyze and interpret the data.
4. How does damping affect the resonance frequency in spring plots?
Damping affects the resonance frequency in spring plots by decreasing it. As the damping coefficient increases, the amplitude of the oscillations decreases, causing the resonance frequency to shift to a lower value. This is because the damping force is absorbing some of the energy from the system, resulting in a decrease in amplitude and frequency.
5. What are some real-life applications of damped spring plots?
Damped spring plots have many real-life applications, such as in shock absorbers for cars and buildings, musical instruments, and earthquake-resistant structures. They are also used in studying and understanding the behavior of various mechanical and electrical systems.
Similar threads
-
Classical Physics
- Replies
- 8
- Views
- 2K
-
Mechanical Engineering
- Replies
- 3
- Views
- 2K
-
Mechanical Engineering
- Replies
- 1
- Views
- 1K
-
Mechanical Engineering
- Replies
- 3
- Views
- 5K
-
Calculus and Beyond Homework Help
- Replies
- 1
- Views
- 1K
-
Mechanical Engineering
- Replies
- 26
- Views
- 2K
-
General Math
- Replies
- 17
- Views
- 4K
-
Introductory Physics Homework Help
- Replies
- 2
- Views
- 3K
-
STEM Career Guidance
- Replies
- 2
- Views
- 15K
-
Quantum Interpretations and Foundations
- Replies
- 25
- Views
- 1K
Share: