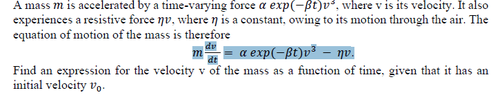Homework Help Overview
The discussion revolves around a differential equation related to physics, specifically focusing on the behavior of a variable with respect to time. The subject area includes ordinary differential equations (ODEs) and their applications in physical contexts.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory, Conceptual clarification, Mathematical reasoning
Approaches and Questions Raised
- Participants express a desire for guidance on solving the given ODE, with some seeking a detailed working guide. There is also a mention of using an integrating factor as a potential approach.
Discussion Status
The discussion is ongoing, with participants actively seeking help and clarification on the problem. Some guidance has been offered regarding the use of an integrating factor, but no consensus has been reached on the best approach to take.
Contextual Notes
There is a mention of a correction regarding the relationship between aerodynamic force and velocity, indicating that assumptions about the problem setup may be under review.