- #1
brainbaby
- 228
- 5
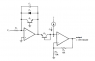
In the figure it could also be possible to connect the transistor Q1 as a diode by shorting its collector with its base ..but instead it is done by keeping both base and collector at ground...
The text have to say that if it would be connected the other way(i.e by shorting collector and base )then the base current would have caused an error ( Base current error ) .
Which type of error is the author talking about..?
Why and how does the error manifest itself...?
Please help!
The text have to say that if it would be connected the other way(i.e by shorting collector and base )then the base current would have caused an error ( Base current error ) .
Which type of error is the author talking about..?
Why and how does the error manifest itself...?
Please help!