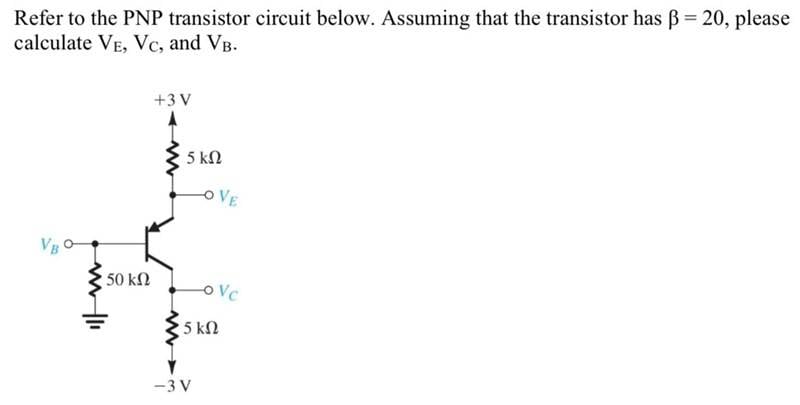
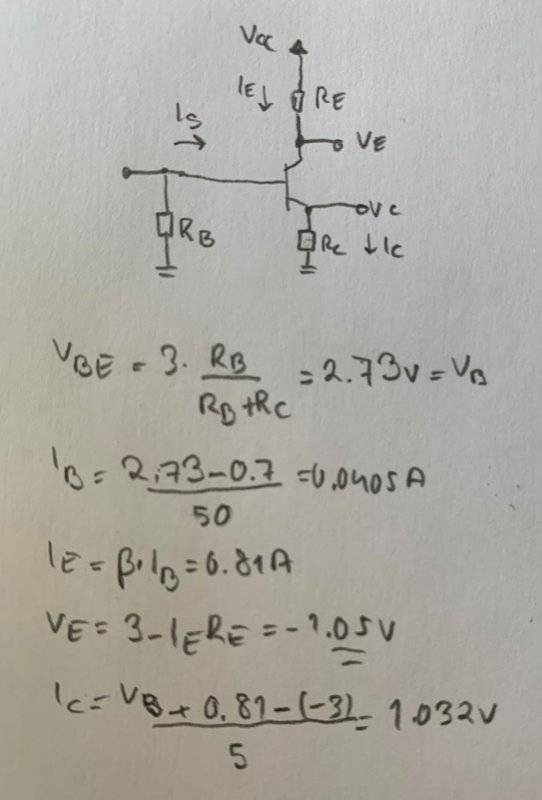SUMMARY
The relationship between Veb and Ie in a PNP transistor is defined by the equation Veb = Ve - Vb, where Veb is typically 0.7 volts. To calculate the emitter current (Ie), apply Ohm's Law to both the emitter voltage (Ve) and the base voltage (Vb), treating Ie as the only unknown variable. The emitter current can be expressed as Ie = 21 * Ib, where Ib is the base current. This relationship is crucial for understanding the operation of PNP transistors in electronic circuits.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of PNP transistor operation
- Knowledge of Ohm's Law
- Familiarity with current amplification concepts
- Basic circuit analysis skills
NEXT STEPS
- Study the characteristics of PNP transistors in detail
- Learn about current gain (beta) in transistors
- Explore circuit design involving PNP transistors
- Investigate the impact of temperature on transistor performance
USEFUL FOR
Electronics students, circuit designers, and engineers working with transistor-based circuits will benefit from this discussion.