SUMMARY
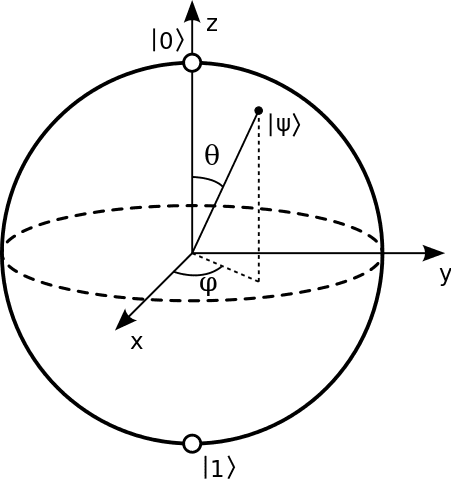
The discussion centers on calculating the coordinates of a qubit's mixed state on the Bloch ball using its density matrix representation. The density matrix is expressed as ##\rho=p_{00}|0\rangle \langle 0|+p_{01}|0\rangle \langle 1|+p_{10}|1\rangle \langle 0|+p_{11}|1\rangle \langle 1|##. Participants confirm that diagonalizing the density matrix is necessary to derive the coordinates using the formula ##(\sum p_i x_i, \sum p_i y_i,\sum p_i z_i)##. A practical method for conversion from the qubit density matrix to the Bloch vector is provided, emphasizing that the process involves straightforward arithmetic operations.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of qubit density matrices
- Familiarity with the Bloch sphere representation
- Basic knowledge of complex numbers and their operations
- Experience with linear algebra concepts, particularly matrix diagonalization
NEXT STEPS
- Study the process of diagonalizing density matrices in quantum mechanics
- Learn about the mathematical properties of the Bloch sphere
- Explore the implications of mixed states in quantum computing
- Investigate the use of Python for quantum state manipulation, particularly using libraries like Qiskit
USEFUL FOR
Quantum computing enthusiasts, physicists, and software developers working with quantum algorithms who seek to understand the representation of qubit states on the Bloch sphere.