Eitan Levy
- 259
- 11
Homework Statement
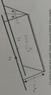
We have two very long wires, each with the same mass of 20 grams per meter. They are hung from the ceiling with two identical wires. When they both had the same current flowing to the opposite directions, they created the same angle.
We double the current in one of them, is the angle that they will create (as shown in the picture) will be the same again?
Homework Equations
F=BIL
The Attempt at a Solution
I couldn't prove it. I am stuck with T1sinθ1=T2sinθ2.
Is there any assumption I am supposed to make? I know that the forces are tension, gravity and magnetic force, and I understand what their directions are.