- #1
Lordgraver
- 2
- 0
Can someone explain me why we could put pi, μi and μiο in
this equation:
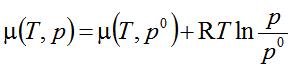
and we get this:
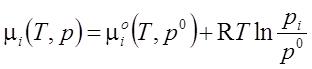
(this is The chemical potential of a component in a perfect mixture of ideal gases wher pi is
partial pressure)
this equation:
and we get this:
(this is The chemical potential of a component in a perfect mixture of ideal gases wher pi is
partial pressure)