Lambda96
- 233
- 77
Hi,
I am currently preparing for my exam and have just watched a video about motion in phase space.
From minute 4 a quadratic potential is introduced and then from minute 6 minute the phase trajectory.
Here are the pictures
quadratic potential
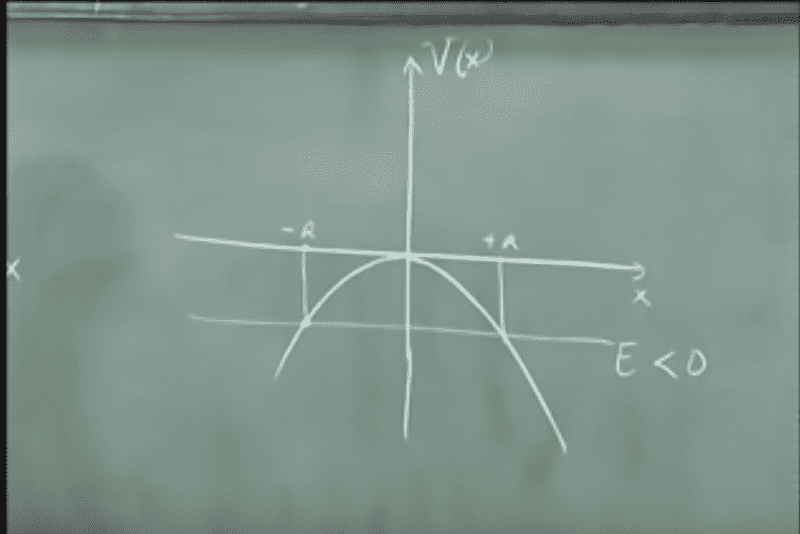
phase trajectory
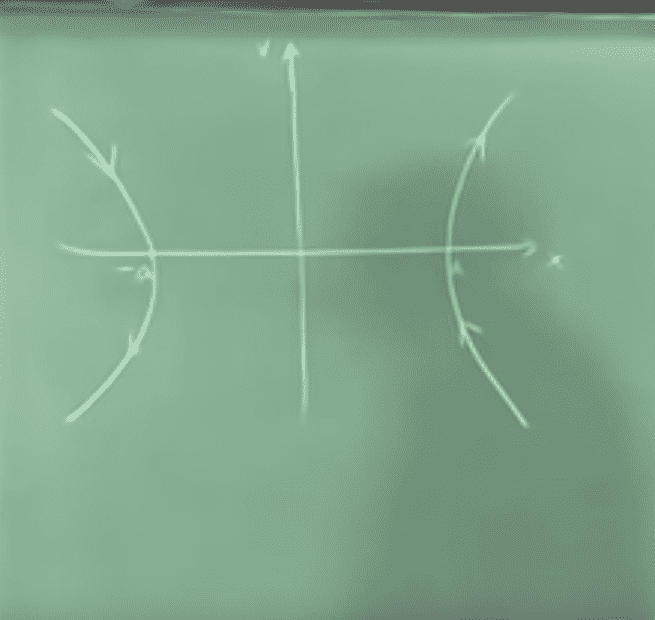
Regarding phase trajectory on the left side, I understand that these are pointing downwards, but I don't understand why the phase trajectory on the right side is pointing upwards, I would say that these must also be pointing downwards, as the potential is unstable and no matter where I place a test particle, it will always accelerate downwards towards the potential.
I am currently preparing for my exam and have just watched a video about motion in phase space.
From minute 4 a quadratic potential is introduced and then from minute 6 minute the phase trajectory.
Here are the pictures
quadratic potential
phase trajectory
Regarding phase trajectory on the left side, I understand that these are pointing downwards, but I don't understand why the phase trajectory on the right side is pointing upwards, I would say that these must also be pointing downwards, as the potential is unstable and no matter where I place a test particle, it will always accelerate downwards towards the potential.