mathmari
Gold Member
MHB
- 4,984
- 7
Hey! 
One box contains ten production parts, four of which have a production error.
Three parts are removed from the box one after the other without putting them back. We consider the following events :
A : the first production part that is removed is OK
B : the second production part that is removed is OK
C : the third production part that is removed is OK
Do we get the below diagramm?
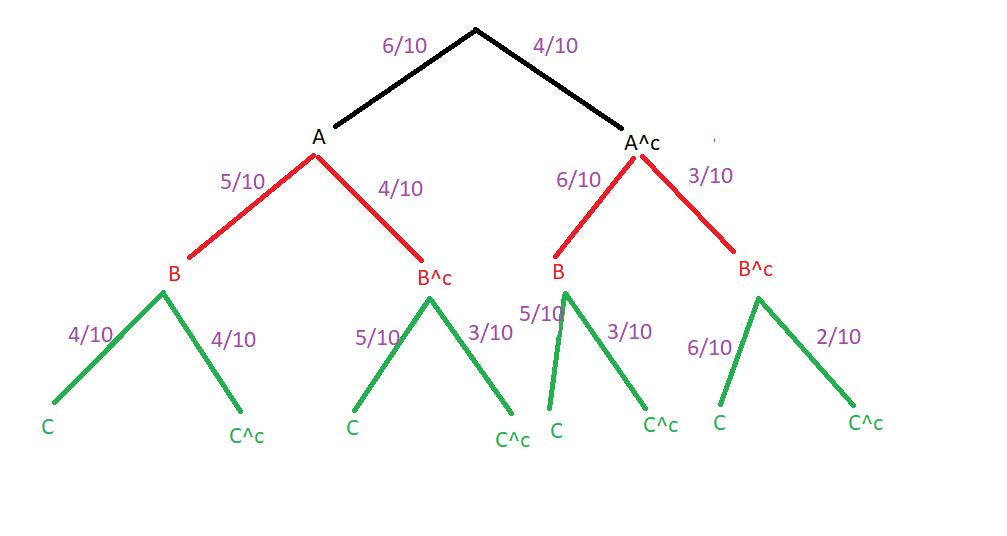
:unsure:
One box contains ten production parts, four of which have a production error.
Three parts are removed from the box one after the other without putting them back. We consider the following events :
A : the first production part that is removed is OK
B : the second production part that is removed is OK
C : the third production part that is removed is OK
Do we get the below diagramm?
:unsure:
Last edited by a moderator: