Guest432
- 48
- 2
The answer here shows the answer as being
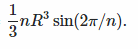
but my limited knowledge of integrals begs me to asks where did the z go?
but my limited knowledge of integrals begs me to asks where did the z go?