SUMMARY
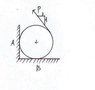
The key step to solving the cylinder friction problem involves determining the angle that force P makes with the horizontal axis. The weight of the cylinder is 400N, the radius is 150mm, and the coefficient of friction is 0.2. A free body diagram is essential for visualizing the forces acting on the cylinder, including normal and frictional forces. By resolving force P into its X and Y components and summing the forces and moments, one can derive the necessary equations to solve for P, which is the force required to initiate rotation.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of free body diagrams
- Knowledge of force resolution into components
- Familiarity with summing forces and moments
- Basic geometry, specifically properties of triangles
NEXT STEPS
- Learn how to construct and analyze free body diagrams
- Study the principles of force resolution in physics
- Explore equations of motion and equilibrium in mechanics
- Review geometric properties of triangles, particularly 3-4-5 triangles
USEFUL FOR
Students in physics or engineering courses, particularly those focusing on mechanics, as well as professionals involved in mechanical design and analysis of rotating systems.