SUMMARY
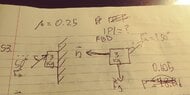
The discussion focuses on calculating the magnitude of force P required to keep a 3.00 kg block stationary against a wall at a 50.0-degree angle. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the wall is 0.250. The analysis involves resolving forces in both the horizontal and vertical directions, establishing that the normal force N must balance the horizontal component of the applied force P. Additionally, the friction force acting downward is defined as f = μN, where μ is the coefficient of static friction.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of static friction and its coefficient
- Knowledge of force resolution in physics
- Familiarity with Newton's laws of motion
- Ability to analyze free-body diagrams
NEXT STEPS
- Calculate the normal force N in terms of the applied force P
- Explore the implications of static friction on block stability
- Learn about free-body diagram techniques for complex systems
- Investigate the effects of varying angles on force calculations
USEFUL FOR
Physics students, engineers, and anyone studying mechanics or force analysis in static systems will benefit from this discussion.