You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
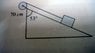
Work done by Tension Ques: Friction 0.5n
AI Thread Summary
The discussion focuses on calculating the speed of a block sliding down an incline after moving 100 cm, using energy conservation principles. A frictional force of 0.5 N is acting on the block, raising the question of whether the work done by tension should be included in the calculations. The total energy before and after the block moves is set to zero, leading to the equation that balances force times distance, kinetic energy, and potential energy. The vertical distance fallen, denoted as h, is also a critical factor in the energy equation. Ultimately, the role of tension in doing work is a key point of inquiry in the energy conservation analysis.
Physics news on Phys.org
Spinnor
Gold Member
- 2,227
- 419
Did you give us all the information that you were given?
naman0804
- 2
- 0
yes i did ... i just want to know if tension does work
Spinnor
Gold Member
- 2,227
- 419
Before the block moves you can set the total energy to zero, after the block has moved 1m the total energy is still zero and is,
0 = .5N X 1m + mV^2/2 - mgh = force times distance + kinetic energy - potential energy
where h is the vertical distance the block falls.
0 = .5N X 1m + mV^2/2 - mgh = force times distance + kinetic energy - potential energy
where h is the vertical distance the block falls.
I multiplied the values first without the error limit. Got 19.38. rounded it off to 2 significant figures since the given data has 2 significant figures. So = 19.
For error I used the above formula. It comes out about 1.48. Now my question is. Should I write the answer as 19±1.5 (rounding 1.48 to 2 significant figures) OR should I write it as 19±1. So in short, should the error have same number of significant figures as the mean value or should it have the same number of decimal places as...
Let's declare that for the cylinder,
mass = M = 10 kg
Radius = R = 4 m
For the wall and the floor,
Friction coeff = ##\mu## = 0.5
For the hanging mass,
mass = m = 11 kg
First, we divide the force according to their respective plane (x and y thing, correct me if I'm wrong) and according to which, cylinder or the hanging mass, they're working on.
Force on the hanging mass
$$mg - T = ma$$
Force(Cylinder) on y
$$N_f + f_w - Mg = 0$$
Force(Cylinder) on x
$$T + f_f - N_w = Ma$$
There's also...
This problem is two parts. The first is to determine what effects are being provided by each of the elements - 1) the window panes; 2) the asphalt surface. My answer to that is
The second part of the problem is exactly why you get this affect.
And one more spoiler:
Similar threads
- Replies
- 7
- Views
- 3K
- Replies
- 2
- Views
- 973
- Replies
- 4
- Views
- 3K
- Replies
- 29
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 16
- Views
- 990
- Replies
- 23
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 58
- Views
- 5K
- Replies
- 3
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 47
- Views
- 3K
- Replies
- 4
- Views
- 2K
Hot Threads
-
The problem of one tube and two balls on a plane
- Started by crazy lee
- Replies: 60
- Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
Collision of a bullet on a rod-string system: query
- Started by palaphys
- Replies: 70
- Introductory Physics Homework Help
Recent Insights
-
Insights Quantum Entanglement is a Kinematic Fact, not a Dynamical Effect
- Started by Greg Bernhardt
- Replies: 7
- Quantum Physics
-
Insights What Exactly is Dirac’s Delta Function? - Insight
- Started by Greg Bernhardt
- Replies: 0
- General Math
-
Insights Relativator (Circular Slide-Rule): Simulated with Desmos - Insight
- Started by Greg Bernhardt
- Replies: 1
- Special and General Relativity
-
Insights Fixing Things Which Can Go Wrong With Complex Numbers
- Started by PAllen
- Replies: 7
- General Math
-
Insights Fermat's Last Theorem
- Started by fresh_42
- Replies: 91
- General Math
-
Insights Why Vector Spaces Explain The World: A Historical Perspective
- Started by fresh_42
- Replies: 0
- General Math