You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
What is Mirror: Definition and 648 Discussions
A mirror is an object that reflects an image. Light that bounces off a mirror will show an image of whatever is in front of it, when focused through the lens of the eye or a camera. Mirrors reverse the direction of the image in an equal yet opposite angle from which the light shines upon it. This allows the viewer to see themselves or objects behind them, or even objects that are at an angle from them but out of their field of view, such as around a corner. Natural mirrors have existed since prehistoric times, such as the surface of water, but people have been manufacturing mirrors out of a variety of materials for thousands of years, like stone, metals, and glass. In modern mirrors, metals like silver or aluminum are often used due to their high reflectivity, applied as a thin coating on glass because of its naturally smooth and very hard surface.
A mirror is a wave reflector. Light consists of waves, and when light waves reflect off the flat surface of a mirror, those waves retain the same degree of curvature and vergence, in an equal yet opposite direction, as the original waves. The light can also be pictured as rays (imaginary lines radiating from the light source, that are always perpendicular to the waves). These rays are reflected at an equal yet opposite angle from which they strike the mirror (incident light). This property, called specular reflection, distinguishes a mirror from objects that diffuse light, breaking up the wave and scattering it in many directions (such as flat-white paint). Thus, a mirror can be any surface in which the texture or roughness of the surface is smaller (smoother) than the wavelength of the waves.
When looking at a mirror, one will see a mirror image or reflected image of objects in the environment, formed by light emitted or scattered by them and reflected by the mirror towards one's eyes. This effect gives the illusion that those objects are behind the mirror, or (sometimes) in front of it. When the surface is not flat, a mirror may behave like a reflecting lens. A plane mirror will yield a real-looking undistorted image, while a curved mirror may distort, magnify, or reduce the image in various ways, while keeping the lines, contrast, sharpness, colors, and other image properties intact.
A mirror is commonly used for inspecting oneself, such as during personal grooming; hence the old-fashioned name looking glass. This use, which dates from prehistory, overlaps with uses in decoration and architecture. Mirrors are also used to view other items that are not directly visible because of obstructions; examples include rear-view mirrors in vehicles, security mirrors in or around buildings, and dentist's mirrors. Mirrors are also used in optical and scientific apparatus such as telescopes, lasers, cameras, periscopes, and industrial machinery.
The terms "mirror" and "reflector" can be used for objects that reflect any other types of waves. An acoustic mirror reflects sound waves. Objects such as walls, ceilings, or natural rock-formations may produce echos, and this tendency often becomes a problem in acoustical engineering when designing houses, auditoriums, or recording studios. Acoustic mirrors may be used for applications such as parabolic microphones, atmospheric studies, sonar, and sea floor mapping. An atomic mirror reflects matter waves, and can be used for atomic interferometry and atomic holography.
View More On Wikipedia.org
A mirror is a wave reflector. Light consists of waves, and when light waves reflect off the flat surface of a mirror, those waves retain the same degree of curvature and vergence, in an equal yet opposite direction, as the original waves. The light can also be pictured as rays (imaginary lines radiating from the light source, that are always perpendicular to the waves). These rays are reflected at an equal yet opposite angle from which they strike the mirror (incident light). This property, called specular reflection, distinguishes a mirror from objects that diffuse light, breaking up the wave and scattering it in many directions (such as flat-white paint). Thus, a mirror can be any surface in which the texture or roughness of the surface is smaller (smoother) than the wavelength of the waves.
When looking at a mirror, one will see a mirror image or reflected image of objects in the environment, formed by light emitted or scattered by them and reflected by the mirror towards one's eyes. This effect gives the illusion that those objects are behind the mirror, or (sometimes) in front of it. When the surface is not flat, a mirror may behave like a reflecting lens. A plane mirror will yield a real-looking undistorted image, while a curved mirror may distort, magnify, or reduce the image in various ways, while keeping the lines, contrast, sharpness, colors, and other image properties intact.
A mirror is commonly used for inspecting oneself, such as during personal grooming; hence the old-fashioned name looking glass. This use, which dates from prehistory, overlaps with uses in decoration and architecture. Mirrors are also used to view other items that are not directly visible because of obstructions; examples include rear-view mirrors in vehicles, security mirrors in or around buildings, and dentist's mirrors. Mirrors are also used in optical and scientific apparatus such as telescopes, lasers, cameras, periscopes, and industrial machinery.
The terms "mirror" and "reflector" can be used for objects that reflect any other types of waves. An acoustic mirror reflects sound waves. Objects such as walls, ceilings, or natural rock-formations may produce echos, and this tendency often becomes a problem in acoustical engineering when designing houses, auditoriums, or recording studios. Acoustic mirrors may be used for applications such as parabolic microphones, atmospheric studies, sonar, and sea floor mapping. An atomic mirror reflects matter waves, and can be used for atomic interferometry and atomic holography.
View More On Wikipedia.org
-

Stargazing Dust on the Mirror: Is Cleaning Worth the Risk?
I keep reading the general opinion that the improvement is just not worth the risk if you attempt to clean the mirror on a Newtonian. Clearly, there must be a point at which it really is an important thing to do. I thought I would try a back of fag packet calculation and see where it took me...- sophiecentaur
- Thread
- Replies: 19
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-
E
B Compton’s experiment vs ordinary mirror
Compton hit the electrons in a carbon target with x-rays and measured the changes in the wavelengths of the scattered photons versus their deflected angle. He correlated that with the energy and momentum the incident photon gave to the electron. My question is why does this not happen in...- exmarine
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Experiment Mirror
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
P
Imaging by cylindrical concave mirror
Consider an upright cylindrical concave mirror with a point source located at the focal point of the mirror. By upright I mean that the mirror is plane in the vertical direction and a concavity in the horizontal plane. Now it seems likely that you would see a virtual image of the point source... -
B
1 light year of mirror reflections?
Just a thought...I know it is impossible, but... What would you see in a mirror if you set up millions of mirrors, each reflected to the next mirror (each not too far apart), maybe in a spiral format, so that the total distance of reflections was one light year. The last mirror was angled to... -

Finding distance of image from mirror given focal length
Homework Statement An object is at a very large distance from a concave mirror of focal length 40cm. Find the distance from the image to the mirror. Is the image real or virtual? Homework Equations 1/u + 1/v = 1/f The Attempt at a Solution [/B] 1/u + 1/v = 1/40 The image has to be real...- RabbitWho
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Focal Focal length Image Length Mirror
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

How mirror/camera/tv work without human eye like system?
Mirror/camera/TV etc. don't have a complex visual cortex system/perception like our eyes. Human eyes use rod,cone,neuron and above all perception of brain to make image. How come these devices create the same clear images/scenes at their surfaces by themselves without having the advance... -
T
Magnetic Mirror for Neutral Atoms
Homework Statement Consider an infinite sheet of magnetized tape in the x-z plane with a nonuniform periodic magnetization M = cos(2πx/λ), where λ/2 is the distance between the north and south poles of the magnetization along the x-axis. The region outside the tape is a vacuum with no currents...- TeslaCoil137
- Thread
- Replies: 28
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
R
Why my mirror does not reflect converging light?
Hello. Today I used a magnifying glass and observed how it converged sun light to a smaller area. The smaller the area and the more violet was the light diffused by the surface. Why does this happen? Then I used a mirror hoping the small violet point would be reflected, but it didn't happen...- RaamGeneral
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Converging Light Mirror
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Optics
-

Exploring Reflection in a Plane Mirror
1) If the angle of incidence of a ray of light to mirror is 50 degrees, what is the angle of reflection from the mirror? 2) If the angle of incidence of a ray of light to a mirror is 20 degrees, what angle does the light ray make with the mirror when it reflects? 3) If a ray of light makes an...- Coco Hwang
- Thread
- Replies: 11
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
B
Calculating Image Height of Flower in Convex Mirror | Homework Question
1. Homework Statement A convex spherical mirror with a focal length of magnitude 25 cm has a 4.0-cm tall flower placed 100 cm in front of it. What is the height of the image of the flower? a.20 cm b. 1.6 cm c .0.80 cm d. 4.0 cm e. 8.0 cm Homework Equations 1/f=1/do+1/di M=-di/do=hi/ho The...- Brittany King
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Convex Convex mirror Mirror
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
A
Mirror Plane Motor & 5000+ RPM: What Image?
If we take a mirror plane mirror circular and make it to setup with a high speed motor and make it to rotate at a speed of 5000 rpm and more ..what would be the image formed on the miroor if an object is made to be placed. Give me better answer...i don't know [emoji17] [emoji17] [emoji17]- ayushkawad1
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Optics
-
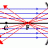
I CMA (Cylindrical Mirror Analyzer)
I'm supposed to be working with a CMA (Cylindrical Mirror Analyzer), but I'm more interested in the physics behind it. This is the instrument in question that we are looking to get: http://www.rbdinstruments.com/products/micro-cma.html We want it to look at different eV levels of different...- RaulTheUCSCSlug
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Atomic and Condensed Matter
-

Stargazing Dealing with Dust and Condensation on Telescope Mirrors
I was examining the insides of my 8" Dobsonian with my new Red Led torch last night and the mirror was looking decidedly dusty. What's the solution to that? A long fluffy duster on a stick? (With care, of course.) I am now thinking that it's probably best to store the scope with the tube...- sophiecentaur
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Mirror
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-
P
Image of a virtual object by a plane mirror
A plane mirror forms a virtual image of a real object placed in front of it and a real image of a virtual object placed in front of it. I can't picture the second case. Please show me a ray diagram showing real image formation by a plane mirror or just explain the case of real image formation by...- physicsmaths1613
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Optics
-
G
Proof of image formation property of spherical mirrors
Hi. I'm trying to proof the image formation property of a concave spherical mirror. I know you can do this easily with a particular choice of rays (namely one that hits the vertex and one that passes through the center of the sphere) but I would like to show that a generic ray yields the same... -
A
With what speed does the object get nearer to the reflection
Homework Statement An object gets closer to the plain mirror with a speed v. With which speed does it get closer to the reflection? Homework Equations l=v*t The Attempt at a Solution As l (length of road) is twice as big l2=2l1, but the time is equal t1=t2, then velocity should be two times...- annalian
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Mirror Reflection Speed
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Lens and mirror combination
Homework Statement A convex lens which focus point is 10 cm is placed face-to-face with plane/flat mirror in a 20 cm distance. If a candle is placed 5 cm in front of the plane mirror which will get reflected by the mirror and refracted by the lens, so the distance between two first image in...- terryds
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Combination Lens Mirror
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
S
Concave mirror: Reflected rays do not meet at one point
I have drawn a diagram of the incident and reflected rays of an object by the concave mirror. Red color shows the incident rays, black color shows the normals drawn from the center of curvature, while green color shows the reflected rays. Shouldn't all the reflected rays meet at one point. Any...- simplescience
- Thread
- Replies: 12
- Forum: Optics
-
A
How to solve for distance of object with a concave mirror?
Homework Statement An object is placed a distance do in front of a concave mirror with a radius of curvature r = 6 cm. The image formed has a magnification of M = 4.3. Solve for the object's distance. Homework Equations M = -di/do (1/do) + (1/di) = 2/R = 1/f The Attempt at a Solution I've tried...- AngelLegs
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Concave Concave mirror Mirror
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
V
Backscatter setup - one way mirror
I'm constructing a backscatter optical setup for my thesis and I'm trying to find something like a pellicle mirror (or pellicle beamsplitter) that is transparent to light from one side but reflects from the other side. I can use a conventional pellicle beamsplitter, however since my... -

B Photon and half-silvered mirror
Suppose we have a photon fired at a half-silvered mirror. There is a 50% chance that the photon reflects, and a 50% chance it passes through, right? Suppose there are two detectors, one that only detects reflected photons and one that detects only passed photons. So my question is: does the...- entropy1
- Thread
- Replies: 17
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-

B What can I expect to see with a 6inch mirror?
I purchased a 6 inch mirror reflector telescope with GPS tracking, and hoping to do some astrophotography. I previously had a 3in lens refractor. Will the resolution be twice as good?- kolleamm
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Mirror
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-

Infinity Focal Points of Plane Mirror
Hello! I've read on several pages that plane mirrors have an infinite amount of focal points. I don't understand? I thought plane mirrors have no focal points because the rays are parallel and don't focus in the first place. Why does a plane mirror have infinity focal points and what does it mean? -
N
Thickness of a partially reflective copper mirror
Hello everyone, We are trying to fabricate a copper layer that is 41% reflective to a beam of 1521nm wavelength. The formula I have used to calculate the thickness is: R = 1 - e-αt Where R: desired reflectance of mirror t: thickness of mirror that would produce said reflectance α... -
V
Position of Final Image in Concave Mirror with Glass Block
Homework Statement A glass block of thickness 60 cm and refractive index 4/3 is placed in front of a concave mirror. A light source is then placed on the center of curvature of the concave mirror. Find the position of the final image formed. (Focal length is 30 cm) Homework Equations...- Volcano
- Thread
- Replies: 13
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
C
Mirror Falling: How Long Can Person See Their Feet?
Homework Statement A plane mirror of length 20 cm is put up in a wall.The upper part of the mirror is 130 cm above the ground.A person is standing 1 m in front of the mirror.The person's eye is 130 cm from the ground.Suddenly,the mirror falls.How long is the person able to see the tip of his...- Carbon123
- Thread
- Replies: 11
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
S
Understanding Particle Movement in a Magnetic Bottle: Field vs. Field Lines
Which is correct? It's almost split 50/50 when I search online. Do the particles trapped in a magnetic bottle travel around the magnetic field or around each magnetic field line? It makes more sense for them to travel around the field because the field is what changes in density not each line...- Samson4
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
A
A Project img on X-Y surface to a cylinder placed in center....
Hi , I came across a problem ,I've search a lot but couldn't exactly find the solution. here is my problem: suppose there is an image ( I call it IMG_A),place IMG_A in the X-Y plane , put a mirror cylinder at the center of IMG_A. what we see in the cylinder mirror is a deform image (I call it...- Amirps
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Differential Geometry
-
Can You See a Photon Beam Between Two Reflective Surfaces?
Let's say you have 2 100% efficient reflective surfaces exactly parallel to each other. If you theoretically managed to place photons at exactly 90° angle of incidence. So this beam of visible light (and I want to stress that) is going to stay there as long as there is no interaction, the beam... -
N
Mirror plane and spin direction
Consider a system with a mirror axis (bulk projected surface), I want to know the direction of spin polarization on the mirror axis. The result is that the spin is perpendicular to the mirror axis, but I don't understand the reason. If someone have related references, please recommend to me... -
M
Why can we not see auroras at lower latitudes?
So I've been thinking about how the magnetic fields from the Earth create a magnetic mirror which accelerates the the particles in the atmosphere causing them to ionize and thus produce the auroras we see. But it is curious to me that they can only be seen in the upper most northern and southern...- MozAngeles
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-
G
Solar Sail/ Mirror Redshift & Blueshift
Hi all, I was hoping you could help me out with this one. Im trying to calculate the redshift or blueshift of a photon that strikes a mirror and reflects. I know E=pc, and that 2p is the momentum transfer. I also know that kinetic energy is 2p/M (of the mirror). However, this says that...- God Plays Dice
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Optics
-
C
Mirror Reflection of a Wave: Analyzing the Outgoing Wave
Hi, In (1+1)D Minkowski spacetime, with coordinates (t,x), let's say there is an incoming plane wave of frequency \omega, \phi_{in}(t,x)=e^{-i\omega (t+x)}. There is a mirror, x=z(t) It reflects the incoming plane wave and emits an outgoing plane wave. Question: why is the outgoing wave...- cedricyu803
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
D
Why does the two concave mirror illusion looks realistic wh
while a simple concave mirror projection does not?Hi, I'm really not sure where does this question go, but perhaps this is as good a place as any... If not, then I would appreciate a referring to the right place. So, I have encountered this nifty, decades old, illusion created by combining two...- disgruntledbot
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Concave Concave mirror Mirror
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Optics
-
D
Image distance after passing through lens and mirror
The lens and mirror in the figure below are separated by d = 1.00 m and have focal lengths of +77.9 cm and -59.0 cm, respectively. An object is placed p = 1.00 m to the left of the lens as shown. i need to find the final object distance and have no idea what am i doing wrong. I am just using the...- Dhananjay97
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Double-slit with half-transparent mirror
Mentor's note: This thread has been split from https://www.physicsforums.com/threads/double-slit-with-semi-transparence.845980 What about if the wall were not transparent but one of the slits equiped with a half transparent mirror ? Then we would half-know which path was taken hence we should...- jk22
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Double-slit Mirror
- Replies: 11
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-

What is the Jones Matrix of a mirror at an angle?
Hi, Concerning optical polarization, what is the Jones Matrix of a mirror at a non-zero angle of incidence with respect to incoming light? For a mirror at normal incidence the matrix is (1 0; 0 -1); How do I incorporate the angle? -
Q
Converging Lens and Plane Mirror Question
Homework Statement A real object is put in-between a convex lens (f = 30.0cm) and a plane mirror as shown in the figure below. Two images of the object are observed : a real image 50.0cm to the left of the lens and a virtual image to the right of the lens. The size of the virtual image is 3.00...- Quattad
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Converging Lens Mirror Plane
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
A
What would the angle φ be for this deflected laser beam?
Homework Statement The mirror in the image below deflects a horizontal laser by angle θ. What is the angle φ if θ = 60°. Homework Equations θi=θr The Attempt at a Solution So I know that, if I draw a line normal to the mirror, that will make it so that the incident angle and the reflected...- aracali
- Thread
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
C
Question about reflecting light off a mirror
Hello all, I've got a question, obviously. I've got a light shining down from directly up above think laser, I want to reflect the light to hit the wall, redirect it 90 degrees. What angle would the mirror need to be to do this? For some reason I'm thinking 45 degrees. Thanks, Kevin S. Chambers- chambers.keivn
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Optics
-
L
Reflected Light at 3D Angle: Shift in Polarization
I've searched high and low for answers to this, and a friend of mine finally pointed me in the right direction. I decided to write a post about it so hopefully others who have the same question will find the answer more easily. When linearly polarized light is reflected at a 3D angle, the... -

Thick convex mirror or a thin one for the anti-theft mirror?
the question in my exam goes like this: should we use a thick convex mirror or a thin one for the anti-theft mirror? the given answer: thin, because a thin convex mirror does not form multiple images can someone please explain to me why a thin spherical mirror does not form multiple images...- heavystray
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Convex Convex mirror Images Mirror
- Replies: 35
- Forum: Optics
-
BJT Current Mirror Homework: Derive Eqn & Simplify w/ Assumptions
Homework Statement 1. Given the above circuit, derive an exact equation for ##I_{out}## in terms of ##I_{REF}, V_{BE1}, V_{BE2}, \beta_1, \beta_2, R_{E1}, R_{E2}## and ##V_{CC}##. Do not make any assumptions. 2. Simplify the equation from part 1 by assuming ##V_{BE1} = V_{BE2}## and that...- STEMucator
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Engineering and Comp Sci Homework Help
-
A
Window reflection when dark out side act like mirror
Why is it that when a light is on in a room with a window made out of glass, and it being dark out side the window. That you cannot see through the window and instead see light being reflected form the room around you. And vice versa when it is darker inside the room and brighter out side you... -

Does Convex Mirror Thickness Affect Focal Length and Image Sharpness?
hello guys, so i want to ask whether the thickness of a convex/concave mirror affect its focal length and the sharpness of image formed? and what really determines the sharpness of image? thanks for replying in advance! :biggrin::biggrin:- heavystray
- Thread
- Replies: 16
- Forum: Optics
-

Image formed from object at focal point of concave mirror
The question posed: "An object is located to the right of a mirror that in concave in its [the object's] direction. If the object sits on the focal point of the mirror, what answer best describes the image formed?" Our class is united in the notion that as the rays would be parallel...- Max Matiauda
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Optics
-
L
Image formed by a plane-concave lens and a concave mirror
Homework Statement An observer looks at an object of height 2 cm through a plane-convex lens of radius 20 cm and refraction index 1.5. There's a concave mirror of radius 30 cm 40 cm behind it, and the object is at the same distance of both the lens and the mirror. Find the images formed by the...- lorele
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
B
Finding the distance of reflection in a mirror
Homework Statement A student wants to find the position of an image in a plane mirror. She sets up the plane mirror with a pin placed vertically a few centimetres in front of it. To find the image the student looks into the mirror at an angle a little further along the mirror. She can see the...- Barclay
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Mirror Reflection
- Replies: 19
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Doppler Effect in Relativity: Mirror vs Lamp
Dear PF Forum, I have a question again about Doppler effect in relativity. Before I ask about mirror and lamp, I want to refresh the discussion again as in my previous thread: https://www.physicsforums.com/threads/doppler-for-light.823942/ The formula for Doppler factor for light is. ##f =...- Stephanus
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
L
Light Polarization Reflected from Parabolic Mirror
Let's say I have a linearly polarized laser beam, and I focus it to a small spot using a parabolic mirror. Does the light retain its polarization at the focal point? Why or why not? I understand that flat mirrors and concave/convex mirrors preserve linear polarization, and I would like to make...