Neutrons Definition and 224 Threads
-

Does an Atom's Type dictate the Protons and Neutrons?
Hi, Does an Atom's Type have to do with the number of protons and neutrons it has? Or are they completely unrelated? Just curious. Thanks :) -
T
B Does having more neutrons in an isotope make it more or les stable?
Does more neutrons in an isotope make it more or less stable? I got two contradicting sources. I am also quite confused overall about the whole isotope business. The definition of an isotope is that it is an atom with the same number of protons but different number of neutrons. For example...- Tangeton
- Thread
- Isotope Neutrons Stable
- Replies: 11
- Forum: High Energy, Nuclear, Particle Physics
-
C
I What is the size of neutrons in a neutron star?
Does the pressure within a neutron star compress the neutrons to a smaller size?- Cato
- Thread
- Neutron Neutron star Neutrons Star
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-

Double-slit experiment: What is the speed of the neutrons?
Homework Statement An experiment was performed in which neutrons were shot through two slits spaced 0.10 mm apart and detected 3.5 m behind the slits. The following figure shows the detector output. Notice the 100 μm scale on the figure. To two significant figures, what was the speed of the...- kamhogo
- Thread
- De broglie wavelength Double-slit Double-slit experiment Experiment Neutrons Speed
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
P
A Liquid Scintillation Counter using U-238 to detect neutrons
I'm trying to make a LSC with U-238 (non-aqueous form) dipped in the scintillating cocktail to detect fast neutrons (no thermals or epithermals, only fast) from a Cf-252 source. How do I calculate the wavelength emerging from the cocktail (assuming U-238 does not react with the cocktail)? Also...- Priyo
- Thread
- Counter Liquid Neutrons Scintillator
- Replies: 1
- Forum: High Energy, Nuclear, Particle Physics
-
J
Electrostatic analysis of cad model of protons neutrons
Could the orbit filling order of electrons be more classical and less quantum? I attached a jpeg and need someone to do a electrostatics analysis of the CAD model version of it. Does anyone have an electrostatics software package and have time to do a finite element analysis on a 3-D part to...- Jeff Driscoll
- Thread
- Analysis Cad Electrostatic Fea Model Neutrons Orbit Protons
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
G
Fission Reaction: How Many Neutrons Needed for Chain Reaction?
a certain fission reaction releases 3 neutrons. how many of these neutrons must go on to produce a subsequent fission if a chain reaction is to be sustained?- gurumi
- Thread
- Fission Neutrons Reaction
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Other Physics Topics
-
A
I What's the fate of neutrons in black hole formation?
I understand how the neutron stars are formed, and why the electron degeneracy pressure collapses as electrons are absorbed by protons, by photo disintegration. However, I'm struggling to grasp what happens when the gravity is large enough to overcome neutron degeneracy pressure. Apparently a...- Aliasa
- Thread
- Black hole Black hole formation Black holes Formation Hole Neutrons
- Replies: 23
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
O
What happens to neutrons in plasma state?
Let's say we have a mol of hellium-3 and we heat it up until it becomes plasma. What happens to the neutrons? Wikipedia does not mention anything about them. It only says that "Plasma is loosely described as an electrically neutral medium of unbound positive and negative particles". Just to make...- Optymistyk
- Thread
- Neutrons Plasma State
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Atomic and Condensed Matter
-
E
Question regarding decay, protons and neutrons
Homework Statement [/B] You find a 1kg piece of rock containing 3 elements: Fakium with 50 protons and 52 neutrons imaginium with 52 protons and 48 neutrons madeupium with 51 protons and 51 neutrons Fakium is known to be radio active, Which of the other two elements could be the decay product...- ezach1
- Thread
- Decay Neutrons Protons
- Replies: 12
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Of Lost Neutrons Within Reactors
How is a continuous chain reaction maintained within a moderator if it is not fissile material? Are the fissile materials mixed with the moderator or are they coalesced at the center of the surrounding moderator? If it is the latter, how would the surrounding moderator allow fissile material to...- Phaeous
- Thread
- Electromagnetic radiation Electromagnetism Lost Moderator Neutron capture Neutrons Radiation
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Nuclear Engineering
-

Containing Free Neutrons: Could it be Done?
I understand that neutron stars arise because of gravitational forces in a collapsing star. But consider an isolated free neutron moving at slow speed. Leaving aside its decay (12m half life), can they be "contained"? If two of them came together, would the strong nuclear force bind them? Is...- Kostik
- Thread
- Neutrons
- Replies: 17
- Forum: High Energy, Nuclear, Particle Physics
-
N
Resting masses of isolated neutrons versus neutrons in atoms
I'm a high school student reading through a book on the discovery of the Higgs boson, and, among several other things, there's one part that I don't understand completely. I understand that the Higgs field is what gives mass to lots of particles that would otherwise be the same without the...- NotJimmy
- Thread
- Atoms Higgs boson Mass Neutron Neutrons Strong interaction
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-

Do Protons and Neutrons Move around in the Nucleus?
Protons and Neutrons vibrate in place, but do they change positions within the nucleus? Let's say that there's a helium atom which has two protons and two neutrons. If the particles were set up on the corners of a square for easy representation with a neutron on the top left and top right, and a...- Ryan Reed
- Thread
- Atom Neutrons Nucleus Protons
- Replies: 40
- Forum: Other Physics Topics
-
P
Exposure rate from thermal neutrons through water
Homework Statement A beam of thermal neutrons (10^12 neutrons per cm^2 second) strikes a 1cm thick water target normal to its surface. The target is a round disk with diameter 20cm. Find the exposure rate (R/second) 100cm beyond the water target (the middle of the disk) from only the...- Phillyfan321
- Thread
- Cylindrical Neutron flux Neutrons Rate Thermal Water
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-

Why extra neutrons make the nucleus unstable?
I understand that having neutrons in nuclei creates additional strong nuclear force which brings protons together, overcoming EM force thus forming different atoms but why extra neutrons bring instability? Wouldn't more strong force mean extra "glue" to hold nuclei together? yet it seems N/P...- skepticwulf
- Thread
- Neutrons Nucleus
- Replies: 3
- Forum: High Energy, Nuclear, Particle Physics
-
D
Neutrons in electromagnetic fields
Consider a moving neutron passing by an electromagnet, will a neutron be deflected? This video seem to show that the neutron would have to be charged in order for it to move- Danyon
- Thread
- Electromagnetic Electromagnetic fields Fields Neutrons
- Replies: 11
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
N
Difference between Delta particles and protons and neutrons
I am trying to figure out the difference between Δ0 and Δ- and the proton and neutron since both appear to have the same combinations of up/down quarks. Deltas have isospin 3/2 and spin angular momentum 3/2 whereas protons and neutrons have isospin 1/2 and spin angular momentum 1/2. I'm...- nigelscott
- Thread
- Delta Difference Neutrons Particles Protons
- Replies: 15
- Forum: High Energy, Nuclear, Particle Physics
-

Can electrons knock out neutrons?
I know that sufficiently energetic protons and photons (1.7MeV) can knock a neutron out of a beryllium nucleus. Can an electron do the same?- Murdock
- Thread
- Electrons Neutrons
- Replies: 10
- Forum: High Energy, Nuclear, Particle Physics
-

Could Dark Matter be composed of neutrons?
I was thinking about the properties of dark matter - how it doesn't seem to interact with any of the forces of the universe except gravity and I was thinking about how neutrinos also don't have any charge and they don't interact with any other forces except the weak force and gravity. I thought... -

Are neutrons in a neutron star relativistic?
As the title of the thread suggests, I'm interested in estimating the velocity distribution of neutrons in neutron star cores. Putting T ~ 10^12K gives v ~ 15%c or more under Boltzmann statistics. Could someone provide more information or a second opinion on this estimate? Thanks.- skujesco2014
- Thread
- Neutron Neutron star Neutrons Relativistic Star
- Replies: 15
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-

Relationship between Ultracold neutrons and neutron stars
Hi, PF: I'm currently about to graduate from my Ph. D. program in Physics and I want to focus my research in theoretical physics. I feel very excited by topics such as Astrophysics and GR, but also low temperature physics, such as superconductivity, bose-einstein condensation, superfluidity...- skujesco2014
- Thread
- Neutron Neutron stars Neutrons Relationship Stars
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-
K
Slow or fast neutrons in LFTRs (Liquid Fluoride Thorium Reactors)
Some nuclear reactors are called fast breeders because: 1. they use fast neutrons, which means the neutrons have more energy than "thermal neutrons", that have the same energy as the surrounding material. 2. they are called "breeders" because they "breed" fuel. U238 is not a fissile atom, but by...- kiskrof
- Thread
- Neutrons
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Nuclear Engineering
-
N
Is there any element that does not absorb neutrons?
Recently I have been researching the topic and I have not found any completely clear answer. To restate my question (as I asked in the title), is there any element that would not absorb neutrons and if not which element has the lowest neutron absorption rate? Thank you.- Nitro Squared
- Thread
- Element Neutrons
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Chemistry
-

What type of fusion reaction generates the most neutrons?
What type of fusion reaction generates the most neutrons? All I've been able to find information for is D-D fusion and D-T fusion.- Warpspeed13
- Thread
- Fusion Fusion reaction Neutrons Reaction Type
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Nuclear Engineering
-
W
How do neutrons bounce off one another?
My understanding of what allows me to touch, say, a desk is that the desk electrons become very near the electrons on my hand and the electric force repels them. However, if I have 2 electrically neutral particles, such as neutrons, why do they not just pass through each other or something...- Wittyname6
- Thread
- Bounce Neutrons
- Replies: 15
- Forum: Mechanics
-

Why free neutrons are unstable?
Outside the nucleus, free neutrons are unstable and have a mean lifetime of 885.7±0.8 s (about 14 minutes, 46 seconds). why??- majid313mirzae
- Thread
- Neutrons
- Replies: 8
- Forum: High Energy, Nuclear, Particle Physics
-
S
Collision of thermal neutrons and Cobalt
Homework Statement The cross section of ##^{59}Co## for capturing the thermal neutrons is ##2000 fm^2##. A ##10g##, thin paper of ##^{59}Co## is radiated for ##100 hours## in reactor with neutron flux ##2\cdot 10^{18} /m^2s##. Density of ##^{59}Co## is ##8.9g/cm^3##. Half life time of...- skrat
- Thread
- Collision Neutrons Thermal
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
S
Neutrons scattering on Silver plate
Homework Statement A 2 mm thick plate of natural Silver absorbs 11% of neutron flux with kinetic energy 1 eV. What is the total scattering cross section for neutrons? ##\rho (Ag)=10500 kg/m^3## and ##M(Ag)=107.9kg/kmol## What is the ratio between the calculated cross section and geometric cross...- skrat
- Thread
- Neutrons Plate Scattering Silver
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

What causes nuclear fission in a collision between two neutrons?
What will happen if we collide two neutrons? As far as I know,since they have no charge, there won't be any repulsive forces. So one neutron will go through the other.:eek: Is this true? What about nuclear fission? Why does the neutron split the nucleus when there are no forces present? -
L
Why only delayed neutrons matter ?
Hi all, I've been seeing this again and again, that delayed neutrons are the ones that are allowing thermal nuclear reactors to work etc. etc. What I do not understand is how are prompt neutrons controlled and how delayed ones are allowed to "do their thing" no problem ? Wiki says...- Leb
- Thread
- Matter Neutrons
- Replies: 7
- Forum: High Energy, Nuclear, Particle Physics
-

Where do the initial neutrons come from?
In atomic bomb there are two hemispheres of fission material (Uranium or Plutonium), they are joined by means of conventional chemical explosives, the necessary critical mass is reached and the atomic bomb explodes, everybody knows this: But is this condition enough? Indeed, the initial...- Eagle9
- Thread
- Initial Neutrons
- Replies: 5
- Forum: High Energy, Nuclear, Particle Physics
-
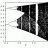
Neutrons and uncertainty principle
Homework Statement Using the Uncertainty Principle show arithmetically that neutrons can't be formed by a proton and an electron. Homework Equations The Attempt at a Solution I can see that if neutrons were made out of a proton and an electron they would just attract each until...- carllacan
- Thread
- Neutrons Principle Uncertainty Uncertainty principle
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
V
Protons Neutrons and Electrons in a neutron star
Hi All, I am preparing for PhD quals and have been looking at problems from other universities. I came across this one and am stumped on how to tackle it. " Assume that the neutron density in a neutron star is 30.1/fm (that is 0.1 neutron per cubic Fermi). Assuming T=0 and ignoring any...- vinceclortho
- Thread
- Electrons Neutron Neutron star Neutrons Protons Star
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Atomic and Condensed Matter
-
M
Are protons and neutrons considered point particles?
I find it confusing, I tried to google the topic but I still don't get it. What is the size and shape of subatomic particles? do they have a size or shape at all? and does the fact that protons and neutrons have larger mass than electrons mean they're bigger in size?- magdi_gamal
- Thread
- Neutrons Particles Point Protons
- Replies: 2
- Forum: High Energy, Nuclear, Particle Physics
-
S
About neutrons and proton in nucleus
sir i want to know why is number of neutron is more or equal number of proton in nucleus of atoms whose atomic number is more tnan one?- shivakumar06
- Thread
- Neutrons Nucleus Proton
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Other Physics Topics
-
M
How many neutrons are in a neutron star with a diameter of 42.0 km?
How many neutrons are in a neutron star with a diameter of 42.0 km? I was under the impression it was just (42.0e3/1e-15)^3 = 7.0048e58 but that's wrong??- MichiganSt35
- Thread
- Diameter Neutron Neutron star Neutrons Star
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
C
How to detect neutrons using Helium 3
I understand that helium 3 has a very high probability of fusing with thermal neutrons, and the reaction produces tritium and hydrogen: n + 3He → 3H + 1H + 0.764 MeV however I do not understand how this reaction is detected. Can someone please explain? Thanks.- CraigH
- Thread
- Helium Neutrons
- Replies: 9
- Forum: High Energy, Nuclear, Particle Physics
-
J
Do Neutrons Emit Infrared Radiation at Room Temperature?
All bodies with a temperature emit electromagnetic radiation also known as thermal radiation or blackbody radiation. If I understand it correctly, the origin of this is the thermal motion (acceleration) of the atoms and their included positive and negative charges leads to EM radiation...- jjschwartz1
- Thread
- Neutrons Radiation Thermal Thermal radiation
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-
V
How protons electrons and neutrons relate to an atom's characteristics
So i was wondering if perhaps a atoms electrons protons and neutrons determine all of its characteristics, such as the hydrogen atom. having only one electron and one proton. it makes it turn into a liquid and solid very close together, and a gas anything above about -259.1°C. and the...- Vacrin
- Thread
- Electrons Neutrons Protons
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Atomic and Condensed Matter
-
1
Scattering of Neutrons from 2d Crystal Lattice
Homework Statement A two-dimensional rectangular crystal has a unit cell with sides a 6.28Å and b 3.14Å. A beam of monochromatic neutrons of wavelength 5.0 Å is used to examine the crystal. Using either the Laue condition for diffraction or Bragg's Law, determine whether it would be...- 1Kris
- Thread
- 2d Crystal Crystal lattice Lattice Neutrons Scattering
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
M
How many strings make up protons, neutrons, and electrons?
So I understand that: Protons= 2 up quarks and a down quark... and Neutrons= an up quark and 2 down quarks... and Electrons are not made of quarks (so small!) So my questions are: 1.) According the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle, we don't know how many strings (according to string...- marshallmeyer1
- Thread
- Electrons Neutrons Protons Strings
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
B
Playing with NEUTRONS. Neutrons thought experiments.
What would happen if: 1- Two neutrons approach each other slowly. Do they glue? 2- A rainfall of neutrons fell to the Earth. I mean very slowly (very low energy) and a huge amount, the same mass as the oceans, i.e. Thank you very much!.- bubal
- Thread
- Experiments Neutrons
- Replies: 12
- Forum: Other Physics Topics
-
S
Protons and neutrons the same mass?
I was wondering, how can both a proton and a neutron weight 1u? An Up quark has a mass of 1.7–3.1 MeV (according to Wikipedia). Down has a mass of 4.1-5.7 MeV. Average Up: 2.4 Average Down: 4.9 If a proton is Up+Up+Down (2.4+2.4+4.9) it has a mass of 9.7 MeV. A neutron is Down+Down+Up...- Sarask
- Thread
- Mass Neutrons Protons
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
A
Electrons, Protons, Neutrons - Build-stones?
Hello. You'll have to excuse my spelling (If I spelled anything wrong), I'm from Sweden and even though I'm told to be good at English, I'm not an expert. I literally just found this forum in my search for some kind of physics forum where I could ask the following question: Are electrons...- alex1532489
- Thread
- Electrons Neutrons Protons
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
K
De Broglie wavelength from scattering of neutrons on crystal
Homework Statement A certain crystal has a set of planes 0.33 nm apart. A beam of neutrons strikes the crystal at normal incidence and the first maximum of the diffraction pattern occurs at ∅= 38°. What is the de Broglie wavelength of the neutrons? Homework Equations nλ = Dsin∅ where D...- kachilous
- Thread
- Crystal De broglie De broglie wavelength Neutrons Scattering Wavelength
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Can anyone explain to me how Deuterium slows down neutrons?
Hey all, First off, am I correct in saying (generally) that Deuterium slows down neutrons? That's why nuclear reactors use it because its easier to catch neutrons that are going slower. ?? Does this apply to all neutrons? Example, let's say I drank a nice tall glass of delicious Heavy...- nukeman
- Thread
- Deuterium Explain Neutrons
- Replies: 12
- Forum: Other Physics Topics
-
A
Number of neutrons & stability?
Hi everyone. I'm kind of new here, please be nice. So I was reading up some physics and came across the fact that if the no. of neutrons is too high compared to the no. of protons, the nucleus becomes unstable. I can understand why this happens with protons, due to the coloumbic repulsion...- almondsize
- Thread
- Neutrons Stability
- Replies: 15
- Forum: High Energy, Nuclear, Particle Physics
-
C
Uncertainly Principle Fast Neutrons
Hey everyone, I've been trying to figure out what went wrong here for abit now and I think maybe a fresh pair of eyes might help. If anyone could point me in the direction of my error that would be great. Thanks Homework Statement An effective treatment for some cancerous tumors is...- CGallin
- Thread
- Neutrons Principle
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Biology and Chemistry Homework Help
-
F
How do neutrons gain energy from phonon scattering?
So during neutron scattering in a crystal, a neutron can interact with 0, 1, or more phonons. First of all, what is the actual mechanism by which they interact? My textbook just kind of glosses over that. Second of all, when a neutron goes in it can absorb a phonon and come out with more...- FillBill
- Thread
- Energy Gain Neutrons Phonon Scattering
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Atomic and Condensed Matter