Discussion Overview
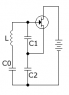
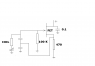
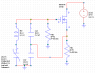
The discussion revolves around the design of a Clapp oscillator circuit using NMOS transistors, focusing on the resonant frequency calculation, biasing networks, and circuit modeling. Participants explore theoretical and practical aspects of oscillator design, including component selection and circuit behavior at different frequencies.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory
- Technical explanation
- Debate/contested
- Mathematical reasoning
- Homework-related
Main Points Raised
- Some participants discuss the need to derive the formula for resonant frequency and question whether to use small-signal equivalent circuits for NMOS transistors.
- There is mention of the importance of the source resistor in the feedback network and its impact on circuit stability.
- One participant expresses confusion regarding the presence of AC signals in the circuit, clarifying that the oscillator generates AC but is powered by DC.
- Participants suggest using specific values for inductors and capacitors to achieve oscillation at lower frequencies, while noting that the circuit may not typically operate at 2.43 GHz.
- Some participants propose using T-models for NMOS to analyze output and input impedances, while others provide formulas for calculating resonant frequency based on inductor and capacitor values.
- There is a discussion about the challenges of biasing networks and the necessity of ensuring proper DC conditions for oscillation.
- One participant mentions the need for impedance matching and the use of transmission lines at higher frequencies, indicating a shift in design considerations.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express various viewpoints on the design and operation of the Clapp oscillator, with no consensus reached on the best approach or specific component values for the intended frequency of 2.43 GHz. Some participants agree on the importance of DC biasing and resonant frequency calculations, while others highlight differing opinions on the circuit's operational frequency range and modeling techniques.
Contextual Notes
Limitations include unresolved assumptions regarding the circuit's operational frequency, the complexity of biasing networks, and the appropriateness of using certain formulas for resonant frequency at higher frequencies.
Who May Find This Useful
Readers interested in oscillator design, NMOS transistor modeling, and resonant frequency calculations may find this discussion relevant.