SUMMARY
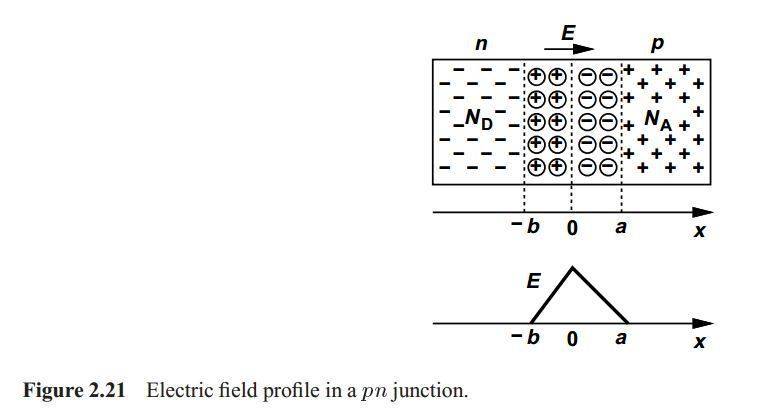
The electric field inside a PN junction in equilibrium approaches zero as one moves away from the depletion region, particularly for x < -b, due to the cancellation of forces from positive and negative ions. The electric field is not strictly zero at the boundary but diminishes rapidly as the distance from the junction increases. The behavior of the electric field can be likened to that of a dipole, where the electric field strength decreases with the cube of the distance from the junction. Understanding these principles is essential for analyzing semiconductor behavior.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of PN junctions and semiconductor physics
- Familiarity with electric fields and dipole theory
- Knowledge of charge distribution in semiconductor materials
- Basic calculus for understanding field strength equations
NEXT STEPS
- Study the behavior of electric fields in semiconductor devices
- Learn about the depletion region and its characteristics in PN junctions
- Explore the mathematical modeling of electric fields using dipole approximations
- Investigate the impact of temperature on PN junction electric fields
USEFUL FOR
Students and professionals in electrical engineering, semiconductor physics, and anyone involved in the design or analysis of electronic components utilizing PN junctions.