- #1
Gigantron
- 11
- 0
1. I made up this problem myself in order to practice. I stumped myself. I'm such a genius, I'm aware
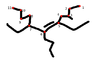
It's basically alkene nomenclature with the E,Z naming scheme.2. Picture
See below. I've taken the liberty of already numbering the longest chain.
Without the double bond, I know that the name of this compound would be 6-butyl-5,7-diethyl-3-methylundecane.
With the double bond, I think it might be (5E)-6-butyl-5,7-diethyl-3-methyl-5-undecene. Is this right? I'm not entirely sure.
It's basically alkene nomenclature with the E,Z naming scheme.2. Picture
See below. I've taken the liberty of already numbering the longest chain.
The Attempt at a Solution
Without the double bond, I know that the name of this compound would be 6-butyl-5,7-diethyl-3-methylundecane.
With the double bond, I think it might be (5E)-6-butyl-5,7-diethyl-3-methyl-5-undecene. Is this right? I'm not entirely sure.
Attachments
Last edited: