- #1
Faelyn
- 3
- 0
- Homework Statement
- What are all of the possible Lewis Dot diagrams for SO4 2-?
- Relevant Equations
- n/a
So I know about the 6 stable resonance Lewis Dot diagrams for sulfate:
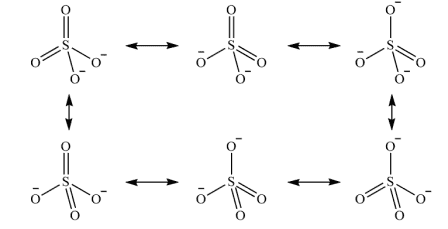
As well as the unstable diagram that only has single bonds between the sulfur and oxygen atoms.But, is it possible for there to be other resonant structures with either 1 or 3 double bonds, even if they're more unstable? I was thinking the one with a single double bond should be possible, but not as much for the three double bonds due to sulfur only having enough valence electrons for six bonds. In both cases the charge is 2- and there are 32 electrons.
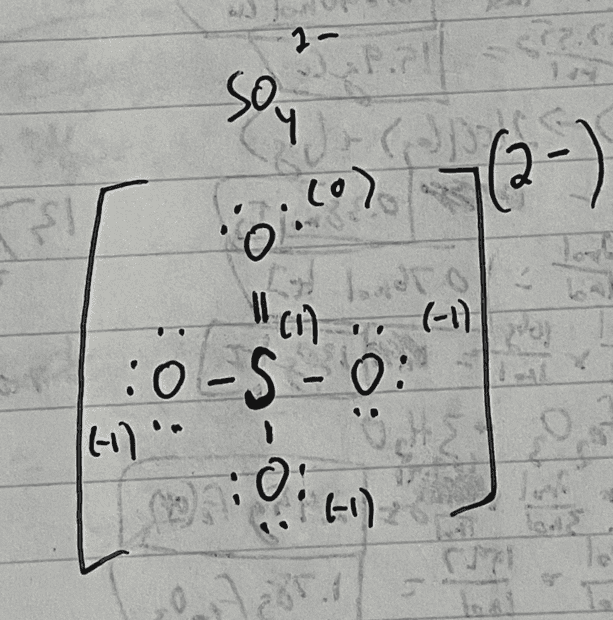
(sulfur is double bonded to only 1 of the oxygen atoms, seems totally possible)
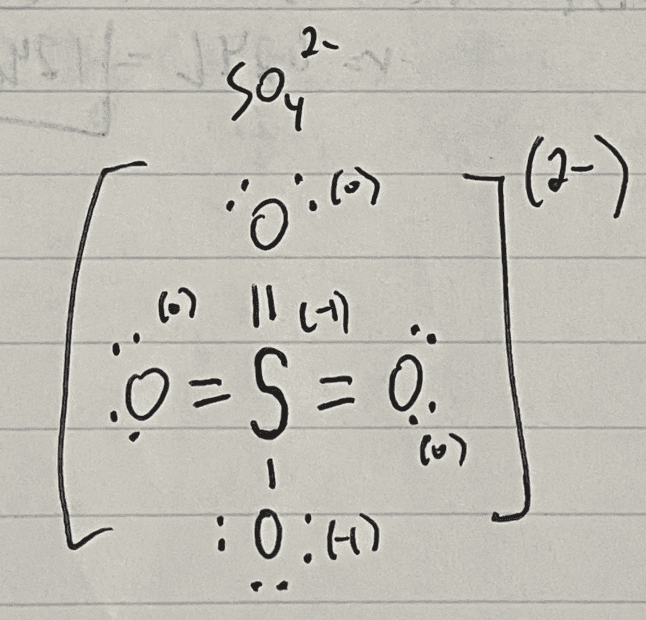
(sulfur is double bonded to 3 of the oxygen atoms, doesn't seem that possible)
As well as the unstable diagram that only has single bonds between the sulfur and oxygen atoms.But, is it possible for there to be other resonant structures with either 1 or 3 double bonds, even if they're more unstable? I was thinking the one with a single double bond should be possible, but not as much for the three double bonds due to sulfur only having enough valence electrons for six bonds. In both cases the charge is 2- and there are 32 electrons.
(sulfur is double bonded to only 1 of the oxygen atoms, seems totally possible)
(sulfur is double bonded to 3 of the oxygen atoms, doesn't seem that possible)