amiras
- 64
- 0
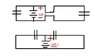
I found this problem in the book and the exact problem is not important, but I don't understand the picture. Book claims that after voltage source is disconnected and switch closed these capacitors in picture are parallel although I tend to think they are in series. (I agree they are in parallel as long as voltage source is connected)
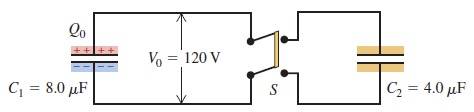
The problem says that after capacitor C1 is charged the power supply (voltage) is disconnected. Also, switch in the middle is insulating handle, charge can only flow between the two upper terminals and between two lower terminals. After switch is closed book claims that capacitors are in parallel.
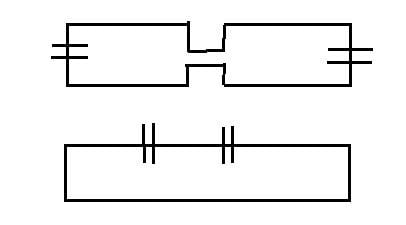
Isn't this circuit now is equivalent to this?
The problem says that after capacitor C1 is charged the power supply (voltage) is disconnected. Also, switch in the middle is insulating handle, charge can only flow between the two upper terminals and between two lower terminals. After switch is closed book claims that capacitors are in parallel.
Isn't this circuit now is equivalent to this?