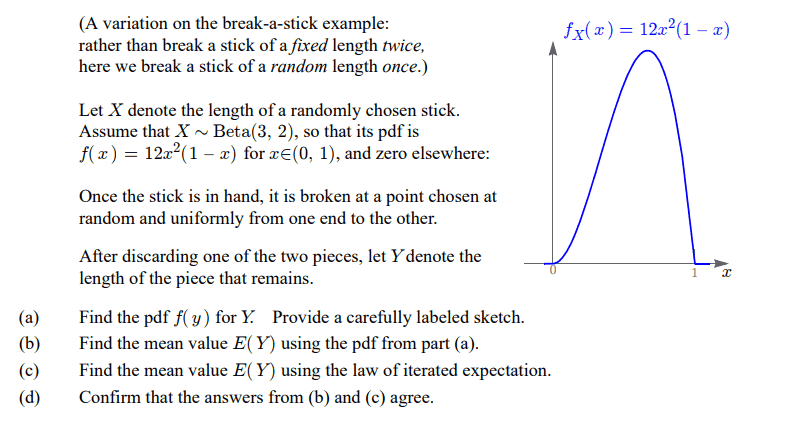
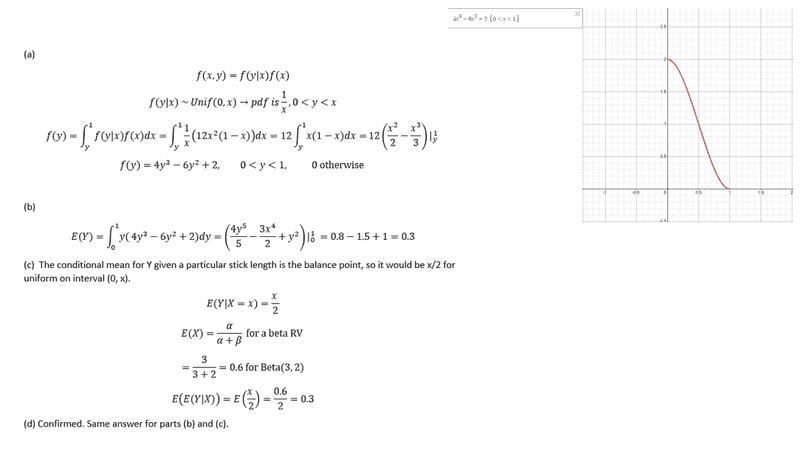
SUMMARY
The discussion focuses on the correct approach to solving a random variables problem involving the cumulative probability function and probability density function. The participant emphasizes the necessity of calculating the cumulative probability function, defined as ##F_Y(y) = Prob(Y\leq y)##, before deriving the probability density function using the formula ##f_Y(y) = \frac d{dy} F_Y(y)##. They highlight the importance of accurately setting integration limits and suggest visualizing the integration region on an x-u plane to understand the trapezium shape, which requires breaking the inner integral into two parts.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of cumulative probability functions (CPFs)
- Knowledge of probability density functions (PDFs)
- Familiarity with double integrals in calculus
- Ability to visualize integration regions in a coordinate plane
NEXT STEPS
- Study the derivation of cumulative probability functions in probability theory
- Learn about the properties and applications of probability density functions
- Practice solving double integrals with varying limits
- Explore graphical methods for visualizing integration regions in calculus
USEFUL FOR
Students and professionals in statistics, mathematicians, and anyone studying probability theory who seeks to deepen their understanding of random variables and integration techniques.