- #1
screen1998
- 3
- 0
Hi, I need help with this.
A non-conducting slab of thickness t, area A and dielectric constant κe is inserted into the space between the plates of a parallel-plate capacitor with spacing d, charge Q and area A, as shown in Figure 7.7.5(a). The slab is not necessarily halfway between the capacitor plates. What is the capacitance of the system?
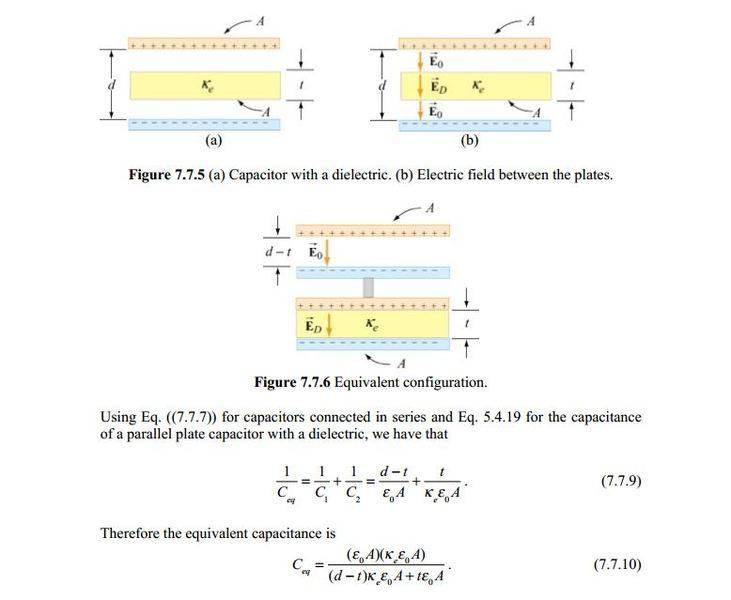
What I don't understand here is the transform from Figurre 7.7.5 to Figure 7.7.6.
How we know that Figure 7.7.6 is the equivalent configuration of Figure 7.7.5?
And why the two dielectrics don't create electric plates because they have different dielectric constants? I know dielectric polarisation but in this case there are two dielectrics with different dielectric constants, therefore I wonder if these electric dipoles will cancel out in the region between two plates of the capacitor.
A non-conducting slab of thickness t, area A and dielectric constant κe is inserted into the space between the plates of a parallel-plate capacitor with spacing d, charge Q and area A, as shown in Figure 7.7.5(a). The slab is not necessarily halfway between the capacitor plates. What is the capacitance of the system?
What I don't understand here is the transform from Figurre 7.7.5 to Figure 7.7.6.
How we know that Figure 7.7.6 is the equivalent configuration of Figure 7.7.5?
And why the two dielectrics don't create electric plates because they have different dielectric constants? I know dielectric polarisation but in this case there are two dielectrics with different dielectric constants, therefore I wonder if these electric dipoles will cancel out in the region between two plates of the capacitor.
Attachments
Last edited: