- #1
Observables
- 15
- 0
Hi all,
I need some help on this one. Some of you may laugh, but it's got me confused. I just can't solve it.
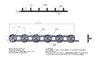
I've attached a jpg of the mechanism with some details about the mass and sizes of the thing.
I have six discs which are liked together by a flat bar, when a torque is applied to the first one, all of the discs rotate, I guess it's a bit like wheels on trains.
Assumptions:
The discs are fixed to a rod at their center's, they can only rotate 90 degrees
The Bars are fixed to the discs at a distance of 50mm from the center of the disc.
The Question is: How do I calculate the force or the torque that it would take to rotate the disc through 90 degrees and back again.
I'm trying to determine the power of a motor that I would need to do the job.
Yours
Obs.
I need some help on this one. Some of you may laugh, but it's got me confused. I just can't solve it.
I've attached a jpg of the mechanism with some details about the mass and sizes of the thing.
I have six discs which are liked together by a flat bar, when a torque is applied to the first one, all of the discs rotate, I guess it's a bit like wheels on trains.
Assumptions:
The discs are fixed to a rod at their center's, they can only rotate 90 degrees
The Bars are fixed to the discs at a distance of 50mm from the center of the disc.
The Question is: How do I calculate the force or the torque that it would take to rotate the disc through 90 degrees and back again.
I'm trying to determine the power of a motor that I would need to do the job.
Yours
Obs.