Calculating Torque for a Rotating Cylinder
Click For Summary
Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around calculating the torque required for a rotating solid cylinder, specifically in the context of a gearbox application. Participants explore various factors influencing torque, including surface speed, moment of inertia, and external forces acting on the cylinder.
Discussion Character
- Technical explanation
- Mathematical reasoning
- Debate/contested
Main Points Raised
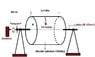
- One participant asks how to calculate the torque on an axle for a solid cylinder rotating at a surface speed of 1 m/s with a mass of 2500 kg.
- Another participant questions the meaning of the 1 m/s speed and states that if the cylinder rotates at constant angular velocity, the torque is zero.
- Some participants clarify that while torque is zero at constant speed, there is a required torque to maintain that speed due to gearbox loads and resistances.
- A participant emphasizes the need for more details about operating conditions to provide a proper answer.
- One participant provides a formula for torque based on moment of inertia and angular acceleration, but another challenges the calculation of moment of inertia and suggests using the standard formula for a solid cylinder.
- There is a discussion about how to consider acceleration timings when designing with induction motors and how that affects the required torque.
- Some participants express confusion about the moment of inertia and its role in calculating torque.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants generally agree that torque is needed to overcome resistances and to accelerate the cylinder, but there is disagreement on the specifics of the calculations and the correct formulas to use. The discussion remains unresolved regarding the exact torque value and the correct approach to the calculations.
Contextual Notes
Participants mention various assumptions, such as the absence of external forces and the need for more details on the operating conditions. There are also unresolved issues regarding the correct moment of inertia and angular acceleration values used in the torque calculations.
Similar threads
- · Replies 12 ·
- · Replies 8 ·
- · Replies 9 ·
- · Replies 4 ·
- · Replies 5 ·
- · Replies 1 ·
- · Replies 7 ·