David Hodge
- 3
- 0
Hi Everybody,
First post on the forum, this one's stumped me I'm afraid. I'm basically trying to model a rotary connection in an AC circuit, and I'm having a bit of trouble with it. Ideally I'd like a reasonable approximation with conventional circuit elements.
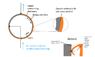
Basically I've got a stationary copper ring and a moving shaft that is vulnerable to lightning strikes. The contact is just a annular faying connection. There's an AC current (from a lightning strike) of variable phase/waveform at ~250 kHz which flows through the moving shaft and into the copper contact ring. I just need a way to model this little snippet of a circuit, hopefully yielding an inductance and impedance value that'll let me size the connection within ~20% or so (so I know what to buy for testing).
Any help is vastly appreciated, especially if you can point out any literature that might describe an empirical model and/or some closed form solution.
I've attached a simplistic diagram of such a rotary interface to try to clarify my question.Thank you!
-DH
First post on the forum, this one's stumped me I'm afraid. I'm basically trying to model a rotary connection in an AC circuit, and I'm having a bit of trouble with it. Ideally I'd like a reasonable approximation with conventional circuit elements.
Basically I've got a stationary copper ring and a moving shaft that is vulnerable to lightning strikes. The contact is just a annular faying connection. There's an AC current (from a lightning strike) of variable phase/waveform at ~250 kHz which flows through the moving shaft and into the copper contact ring. I just need a way to model this little snippet of a circuit, hopefully yielding an inductance and impedance value that'll let me size the connection within ~20% or so (so I know what to buy for testing).
Any help is vastly appreciated, especially if you can point out any literature that might describe an empirical model and/or some closed form solution.
I've attached a simplistic diagram of such a rotary interface to try to clarify my question.Thank you!
-DH