- #1
daphnelee-mh
- 66
- 4
- Homework Statement
- attached below
- Relevant Equations
- listed in the picture
Please help to check whether I did it correct, thanks
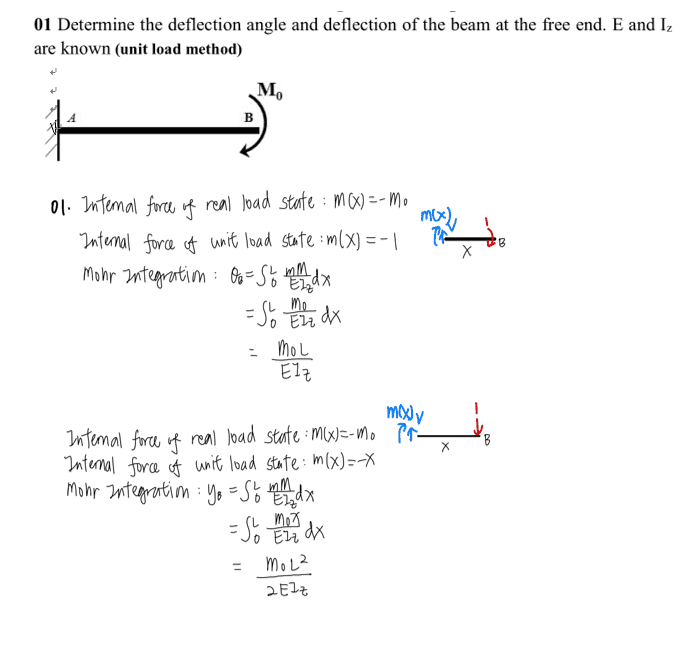
Last edited by a moderator:
Deflection is the amount of bending or displacement that a beam experiences when a load is applied. The deflection angle is the angle formed between the original and deflected position of the beam. In the Unit Load Method, these values are used to calculate the maximum deflection and deflection angle of a cantilever beam under a specific load.
The Unit Load Method involves dividing the beam into smaller sections and calculating the deflection and deflection angle at each section using the formula: D = WL^3 / 3EI, where D is the deflection, W is the applied load, L is the length of the beam, E is the modulus of elasticity, and I is the moment of inertia. The total deflection and deflection angle are then determined by summing up the values for each section.
The Unit Load Method assumes that the beam is linearly elastic, meaning that it follows Hooke's law and has a constant modulus of elasticity. It also assumes that the beam is homogenous and isotropic, meaning that its material properties are the same in all directions. Additionally, the method assumes that the load is applied at a single point and that the beam is not subjected to any external moments.
The Unit Load Method is a simplified approach compared to other methods, such as the Moment-Area Method or the Virtual Work Method. It is often used for quick estimations or for beams with simple load and support configurations. However, it may not provide accurate results for more complex beam designs.
Yes, the Unit Load Method can be used for beams with non-uniform cross-sections by dividing the beam into smaller sections with uniform cross-sections and calculating the deflection and deflection angle for each section. However, this may result in less accurate results compared to using a method specifically designed for non-uniform beams, such as the Moment-Area Method.