- #1
Lindsayyyy
- 219
- 0
Hi everyone
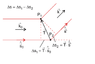
I'm trying to understand the Laue equation but I have problems unterstanding the derivation, especially one part in my textbook about the path difference (see attachment)
My textbook says that the path difference here is:
[tex] \Delta s = \vec T \hat{s_0} - \vec T \hat{s} [/tex]
But why is there a minus? I thought there has to be a plus (like in the derivation of the Bragg equation) because when I look at the picture in the attachment, the ray which is on bottom has to travel dS1 and dS2 in addition. Where is my mistake?
Thanks for your help everyone. If anything is unclear just ask, I know my English is not the best.
Homework Statement
I'm trying to understand the Laue equation but I have problems unterstanding the derivation, especially one part in my textbook about the path difference (see attachment)
The Attempt at a Solution
My textbook says that the path difference here is:
[tex] \Delta s = \vec T \hat{s_0} - \vec T \hat{s} [/tex]
But why is there a minus? I thought there has to be a plus (like in the derivation of the Bragg equation) because when I look at the picture in the attachment, the ray which is on bottom has to travel dS1 and dS2 in addition. Where is my mistake?
Thanks for your help everyone. If anything is unclear just ask, I know my English is not the best.