Sarah0001
- 31
- 1
1. A white light shines vertically down on a horizontal CD ROM disc.
The disc is viewed by a teacher whose eye is a horizontal distance 0.50 m from the disc and 0.35 m vertically above its horizontal plane, Figure 1.2. A yellow light of wavelength 590 nm is observed due to first order diffraction.
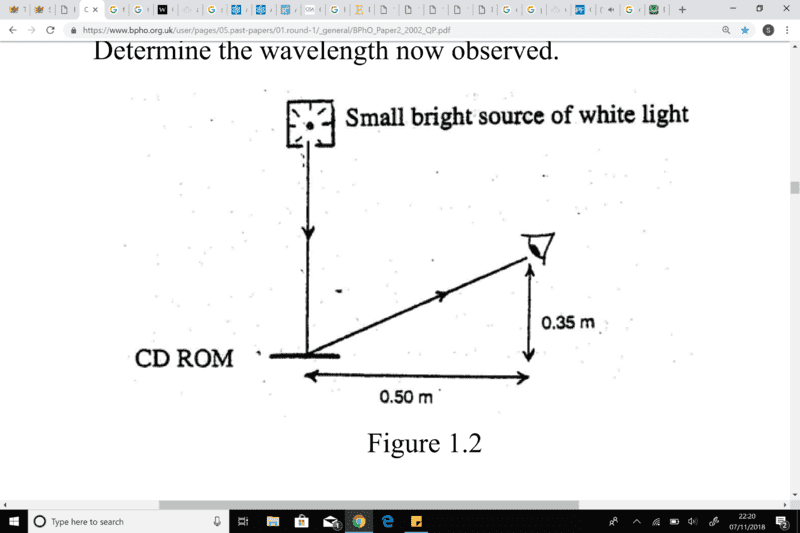 Fig 1.2 Uploaded image
Fig 1.2 Uploaded image
. (i) Deduce the spacing d between adjacent tracks of the CD ROM.
Answer: 720 nm,
angle subtended between incident and reflected ray is 55 degrees
2) relevant equations :

This below part is what I require help with.
(ii) The CD ROM is tilted, clockwise through an angle of 5 degrees . Determine the wavelength now observed.
3. My attempt at the solution :
wavelength = 720*10^-9 * sin 60
Worked solution: (uploaded)

I understand that the angle of incidence ray with mirror is now 95 degrees as opposed to 90,
so 95-55 = 40
so cos theta 1 = wavelength / d , theta 1 is 40, and thus sin theta 2 = wavelength / d , theta two must be 50 degrees by ( 180-90-40).
However I do not understand why 'sin5' is subtracted by sin 50 in the worked solutions, nor do I understand how cos ( 90 - 5) leads to sin (5), or cos(90 -x+5) = sin ( x -5) for that sake
Also fundamentally I cannot understand why the worked solutions initially finds the path difference to equal to (cosine A - Cosine B ) * slit separation (d)
The disc is viewed by a teacher whose eye is a horizontal distance 0.50 m from the disc and 0.35 m vertically above its horizontal plane, Figure 1.2. A yellow light of wavelength 590 nm is observed due to first order diffraction.
. (i) Deduce the spacing d between adjacent tracks of the CD ROM.
Answer: 720 nm,
angle subtended between incident and reflected ray is 55 degrees
2) relevant equations :

This below part is what I require help with.
(ii) The CD ROM is tilted, clockwise through an angle of 5 degrees . Determine the wavelength now observed.
3. My attempt at the solution :
wavelength = 720*10^-9 * sin 60
Worked solution: (uploaded)
I understand that the angle of incidence ray with mirror is now 95 degrees as opposed to 90,
so 95-55 = 40
so cos theta 1 = wavelength / d , theta 1 is 40, and thus sin theta 2 = wavelength / d , theta two must be 50 degrees by ( 180-90-40).
However I do not understand why 'sin5' is subtracted by sin 50 in the worked solutions, nor do I understand how cos ( 90 - 5) leads to sin (5), or cos(90 -x+5) = sin ( x -5) for that sake
Also fundamentally I cannot understand why the worked solutions initially finds the path difference to equal to (cosine A - Cosine B ) * slit separation (d)