bfusco
- 126
- 1
diffraction -- how does it actually work?
In diffraction for light of a single slit, i know that a bright spot appears in the center and subsidiary bright spots to the sides of the central one, but I have a hard time explaining how diffraction works.
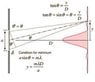
I need some help coming to a satisfactory explanation for why there are dark fringes although the light through the slit propagates in all directions. It was explained to me that dark fringes occur if that angle satisfies asin\theta'=\delta=\lambda (based on the image provided), but i don't really know what that means. I understand that there is a phase difference between the light propagating from all points between the slit that correspond to the difference the light has to travel at each point, but beyond that I don't understand, how does the math i provided describe dark fringes and light fringes?
Also if there is a double slit there are also fringes which have some mathematical relation that similar to the one i stated above, but not the same. I am not sure of the relation and I could really use an explanation.
Thank you in advance.
In diffraction for light of a single slit, i know that a bright spot appears in the center and subsidiary bright spots to the sides of the central one, but I have a hard time explaining how diffraction works.
I need some help coming to a satisfactory explanation for why there are dark fringes although the light through the slit propagates in all directions. It was explained to me that dark fringes occur if that angle satisfies asin\theta'=\delta=\lambda (based on the image provided), but i don't really know what that means. I understand that there is a phase difference between the light propagating from all points between the slit that correspond to the difference the light has to travel at each point, but beyond that I don't understand, how does the math i provided describe dark fringes and light fringes?
Also if there is a double slit there are also fringes which have some mathematical relation that similar to the one i stated above, but not the same. I am not sure of the relation and I could really use an explanation.
Thank you in advance.
Attachments
Last edited: