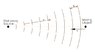- #1
Karol
- 1,380
- 22
Homework Statement
I read that when a body approaches a stationary one which emits radar waves, the wavelength λ2 of the returned waves is longer than λ1, the wavelength of the emitted ones, but I get the opposite. I suppose this is true for sound waves also.
See picture.
The Attempt at a Solution
Velocity of sound in the air: u
Velocity of approaching object: v
The frequency at which the waves from the stationary source hit the moving object:
[tex]f_1=\frac{u+v}{\lambda_1}[/tex]
The wavelength of the reflected wave:
[tex]\lamda_2=\frac{u-v}{f_1}=\frac{(u-v)\lambda_1}{u+v}[/tex]
Now:
[tex]\frac{u-v}{u+v}<1\rightarrow\lambda_1>\lambda_2[/tex]