SUMMARY
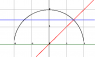
The discussion focuses on evaluating the double integral using polar coordinates for the function ∫sqrt(2)0 ∫sqrt(4-y2) 1/(1+x2+y2) dxdy. The key transformation involves recognizing that the region defined by the limits corresponds to a circle with radius 2, leading to the conversion of the function to 1/(1+r2) and the integration bounds for r being from 0 to 2. The correct polar limits are established as θ ranging from 0 to π/4, confirming the area of integration.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of double integrals in calculus
- Familiarity with polar coordinate transformations
- Knowledge of graphing functions and regions in the Cartesian plane
- Proficiency in using LaTeX for mathematical expressions
NEXT STEPS
- Learn about polar coordinate integration techniques
- Study the properties of circles in polar coordinates
- Explore the use of LaTeX for formatting mathematical equations
- Practice converting Cartesian integrals to polar coordinates with various functions
USEFUL FOR
Students and educators in calculus, mathematicians working with integrals, and anyone interested in mastering polar coordinate transformations for double integrals.