SUMMARY
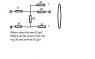
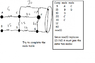
The discussion focuses on calculating the equivalent resistance of a circuit with resistors of 12 ohms, 60 ohms, 30 ohms, and 20 ohms. The correct equivalent resistance at terminals a-b is determined to be 32.5 ohms. Key calculations involve transforming the 12 ohm and 60 ohm resistors in parallel to yield a 10 ohm equivalent, which is then combined with other resistors. Participants emphasize the importance of correctly identifying nodes and maintaining circuit topology during transformations.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of Ohm's Law and basic circuit theory
- Familiarity with series and parallel resistor calculations
- Ability to visualize circuit topology and node connections
- Proficiency in drawing and interpreting circuit diagrams
NEXT STEPS
- Study resistor combinations in series and parallel using practical examples
- Learn about circuit topology and its impact on equivalent resistance
- Explore circuit simulation tools like LTspice for visualizing resistor networks
- Practice labeling nodes and components in complex circuit diagrams
USEFUL FOR
Electrical engineering students, hobbyists working on circuit design, and anyone seeking to improve their understanding of resistor networks and equivalent resistance calculations.