Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around finding the Thévenin equivalent resistance and voltage in a circuit that includes a diode. Participants explore how to simplify the circuit to a model consisting of a DC source, a single resistor, and a diode, while addressing the role of the diode in this process.
Discussion Character
- Homework-related
- Technical explanation
- Conceptual clarification
- Debate/contested
Main Points Raised
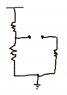
- One participant questions whether to treat the diode as a short circuit or to open circuit it when finding the Thévenin equivalent.
- Several participants inquire about the specific points between which the Thévenin equivalent is to be modeled, particularly regarding the role of a 2.5 kΩ resistor.
- There is a suggestion to simplify the circuit stepwise, starting with the part before the diode.
- Another participant proposes that the circuit can be simplified to a 10V source and a single 10kΩ resistor, but there is uncertainty about the importance of the 2.5 kΩ resistor.
- One participant emphasizes the need to analyze the circuit as a voltage divider, indicating that the two 5kΩ resistors are not in series.
- There is discussion about the output voltage of the diode and whether it refers to the potential drop across the diode or the load resistor.
- Participants express uncertainty about circuit drawing conventions and the implications for analysis.
- One participant concludes that the Thévenin model will consist of a voltage source in series with a resistance and a diode, along with the 2.5 kΩ resistor.
- There is a confirmation that the Thévenin resistance can be calculated as 2.5 kΩ when the voltage source is shorted.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants generally agree on the approach to simplify the circuit and the role of the voltage divider, but there are multiple competing views on how to handle the diode and the specific configuration of the resistors. The discussion remains unresolved regarding the best method to account for the diode in the Thévenin equivalent.
Contextual Notes
Participants express varying levels of familiarity with circuit analysis, which may affect their interpretations and approaches to the problem. There are also unresolved questions about the specifics of the circuit configuration and the role of certain components.