- #1
Numeriprimi
- 138
- 0
Homework Statement
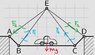
We have this bridge, which is 2D - as shown picture.
How I determine which sticks are subjected to pressure and which tension? How big are these forces? Sticks are intangible, mass of car is M. From the picture, we can determine the length of the sticks.
Picture: http://fykos.cz/rocnik26/obrazky/s4u5_zadani.png
Note: As we proceed, if sticks length density will be p?
2. The attempt at a solution
If one square has length one meter, then:
Line AB, AE, BE, CD, CE, DE I determine by Pythagorean theorem. I think the pressure is only in line BC. In others line is tension.
BC: F= g * m... This is the result for BC?
With the tension, however, I never calculate. I have no idea what to do, although I was looking for, I have not found good formula. Could you please advise me?
Note:
If they have a rod length density, then their weight will be m = p * l
However, that again is all I can think...
Thanks very much and sorry for my bad English.