Kqwert
- 160
- 3
- Homework Statement
- Finding fourrier coefficients by observation
- Relevant Equations
- No eq. posted
Hello,
I need help with question #2 c) from the following link (already LateX-formatted so I save some time...):
https://wiki.math.ntnu.no/_media/tma4135/2017h/tma4135_exo1_us29ngb.pdf
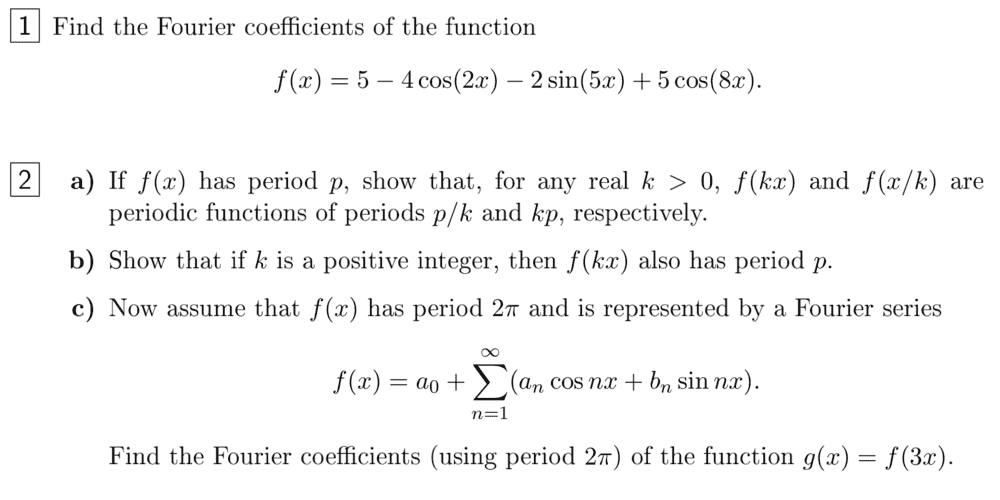
I do understand that the a0 for both expressions must be the same, but what about an and bn? I don't understand how you find them, given that we'll have an*cos(nx)/bn*sin(nx) in the first case while we will have an*cos(3nx)/bn*sin(3nx) in the second case.
I need help with question #2 c) from the following link (already LateX-formatted so I save some time...):
https://wiki.math.ntnu.no/_media/tma4135/2017h/tma4135_exo1_us29ngb.pdf
I do understand that the a0 for both expressions must be the same, but what about an and bn? I don't understand how you find them, given that we'll have an*cos(nx)/bn*sin(nx) in the first case while we will have an*cos(3nx)/bn*sin(3nx) in the second case.
Last edited by a moderator:
 The above is of course bogus. As you debunked correctly in #11:
The above is of course bogus. As you debunked correctly in #11: