- #1
chetzread
- 801
- 1
Homework Statement
http://ocw.nthu.edu.tw/ocw/upload/8/256/Chapter_7-98.pdf refer to page 3
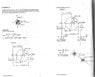
in the 2nd, 3rd pictures, i have problem of finding σx'
Homework Equations
The Attempt at a Solution
why can't use the formula to find σs ?
it's given that σx' = ( σx+ σy)(0.5) + (0.5)( σx- σy)cos2θ + τxy(sin2θ)
= (100+60)(0.5) +(0.5))100-60)(cos60) +52(sin60)
=155
But, the author found σx = 111.6 using Mohr's circle method, why i can't use this method? did i miss out something?