- #1
Meowserkitty
- 14
- 0
Homework Statement
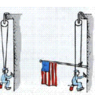
Harry the painter swings year after year from his bosun’s chair. His weight is 575 N and the rope, unknown to him, has a breaking point of 300 N. Why doesn’t the rope break when he is supported as shown at the left below? One day Harry is painting near a flagpole, and, for a change, he ties the free end of the rope to the flagpole instead of to his chair as shown at the right. What happens to Harry and why? (2 pts.)
Homework Equations
fnet=ma
The Attempt at a Solution
To be honest I'm entirely lost. It is more of a conceptual question and I believe the answer may have to do with the forces cancelling each other out. I also believe the rope will snap when on the flag pole (or the pole might) because of the uneven forces.