- #1
twoski
- 181
- 2
Let's say i have a set of lines (denoted in the image as connected at the blue dots) and a rectangle with maxs and mins known (denoted with orange dots).
I want to project from the mins of my rectangle such that i get a point on the line below it (the green dot). Furthermore, this needs to be a general solution (ie if the shapes were all rotated 45 degrees i'd still get the same results).
There must be some trick with cross products or something that I'm not seeing here, any insights?
Here is the picture to help make it clear.
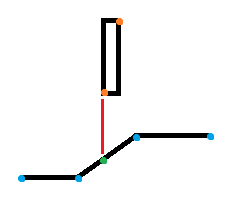
I want to project from the mins of my rectangle such that i get a point on the line below it (the green dot). Furthermore, this needs to be a general solution (ie if the shapes were all rotated 45 degrees i'd still get the same results).
There must be some trick with cross products or something that I'm not seeing here, any insights?
Here is the picture to help make it clear.