- #1
aero_zeppelin
- 86
- 0
Homework Statement
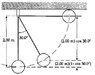
A 400-N child is in a swing that is attached to ropes 2.00 m long. Find the gravitational potential energy of the child–Earth system relative to the child’s lowest position when (a) the ropes are horizontal, (b) the ropes make a 30.0° angle with the vertical, and (c) the child is at the bottom of the circular arc.
Homework Equations
Ug = mgy
The Attempt at a Solution
For a) there was no problem.
For b) I thought it was as simple as applying Ug = mgy cos 30° = (400 N)(2.0 m) cos 30°
But the book says its Ug = mgy (1-cos 30°)
That's my confusion... why 1 - cos 30° and not cos 30° by itself??
any help? Thanks in advance!