- #1
caters
- 229
- 9
My Kepler Bb humanoids have 2 hearts and circulatory systems. If the 2 hearts are out of sync, there is definitely a problem. But I was thinking that a normal heart rate for them might be somewhere in the 40-80 BPM range.
But how could they get heart specific EKGs is what I am really wondering. I mean the conventional cutaneous EKG would not let you know whether the problem is in the right heart, left heart, or both, just that there is a problem. How would they narrow it down? Like if they saw this:
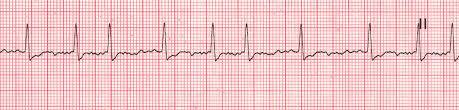
How would they know if it is afib of the right heart, afib of the left heart, afib of both hearts, right heart vfib, or left heart vfib? Any of these 5 or other arrhythmias could make a cutaneous EKG look like the image above.
I am not sure that putting electrodes on the heart itself is best though because likely, that would cause a wandering baseline. But it is the only way I can think of to get a heart specific EKG and not one that is a sum of all the hearts(cutaneous EKG).
Do you have any ideas on this?
I am especially confused about how they would tell normal in sync beats from 1 heart normal and the other asystolic. Those would both look like a normal rhythm. And if 1 and only 1 heart is asystolic, the humanoid will be conscious.
Symptoms are not valid for this since they vary widely from person to person. A good example of this is Sinus Bradycardia where the heart is slow but otherwise normal.
1 person with Sinus Bradycardia might be perfectly fine, even if that person isn't an athlete.
Another person with Sinus Bradycardia at the same heart rate might feel dizzy and lightheaded and possibly loose consciousness(In other words, they might pass out).
So how could they tell if the abnormality is in the right heart, the left heart, or both without risking a wandering baseline? The cutaneous EKG could determine that there is an abnormality and what type(bradycardia, tachycardia, fibrillation, flutter, hearts out of sync) but not the specific abnormality. EKG leads on the hearts themselves could determine the specific abnormality but the baseline would regularly go up and down with ventricular contraction and possibly even atrial contraction. So I need something in between the 2. Something that is heart specific so that left heart vs right heart abnormalities can be determined but also something that doesn't wander so much with ventricular contraction.
But how could they get heart specific EKGs is what I am really wondering. I mean the conventional cutaneous EKG would not let you know whether the problem is in the right heart, left heart, or both, just that there is a problem. How would they narrow it down? Like if they saw this:
How would they know if it is afib of the right heart, afib of the left heart, afib of both hearts, right heart vfib, or left heart vfib? Any of these 5 or other arrhythmias could make a cutaneous EKG look like the image above.
I am not sure that putting electrodes on the heart itself is best though because likely, that would cause a wandering baseline. But it is the only way I can think of to get a heart specific EKG and not one that is a sum of all the hearts(cutaneous EKG).
Do you have any ideas on this?
I am especially confused about how they would tell normal in sync beats from 1 heart normal and the other asystolic. Those would both look like a normal rhythm. And if 1 and only 1 heart is asystolic, the humanoid will be conscious.
Symptoms are not valid for this since they vary widely from person to person. A good example of this is Sinus Bradycardia where the heart is slow but otherwise normal.
1 person with Sinus Bradycardia might be perfectly fine, even if that person isn't an athlete.
Another person with Sinus Bradycardia at the same heart rate might feel dizzy and lightheaded and possibly loose consciousness(In other words, they might pass out).
So how could they tell if the abnormality is in the right heart, the left heart, or both without risking a wandering baseline? The cutaneous EKG could determine that there is an abnormality and what type(bradycardia, tachycardia, fibrillation, flutter, hearts out of sync) but not the specific abnormality. EKG leads on the hearts themselves could determine the specific abnormality but the baseline would regularly go up and down with ventricular contraction and possibly even atrial contraction. So I need something in between the 2. Something that is heart specific so that left heart vs right heart abnormalities can be determined but also something that doesn't wander so much with ventricular contraction.