SUMMARY
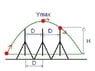
The discussion focuses on calculating the initial and final velocities of a human cannonball projected over three ferris wheels, each 18 meters high, while covering a horizontal distance of 10.63 meters. The initial height of projection is 2.50 meters, and the problem requires finding the minimum initial velocity for a successful stunt. Key equations discussed include the projectile motion equations and the conservation of energy principles, emphasizing that assumptions about the launch distance and angles significantly affect the calculations.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of projectile motion equations
- Familiarity with conservation of energy principles
- Basic algebra and trigonometry for solving equations
- Knowledge of kinematic equations for vertical and horizontal motion
NEXT STEPS
- Study the equations of projectile motion in detail
- Learn about the conservation of energy in projectile motion
- Explore the effects of launch angles on projectile range and height
- Research methods for optimizing projectile trajectories in physics
USEFUL FOR
Students studying physics, particularly those focusing on mechanics and projectile motion, as well as educators looking for practical examples of applying theoretical concepts in real-world scenarios.