Discussion Overview
The discussion centers on the design of feedback control circuits for boost converters, particularly focusing on the role of feedback in maintaining output voltage stability under varying load conditions. Participants explore the implications of duty cycle adjustments and the behavior of the circuit components in response to changes in input and output voltages.
Discussion Character
- Technical explanation
- Debate/contested
- Mathematical reasoning
Main Points Raised
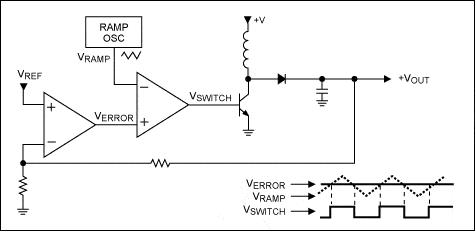
- One participant questions the necessity of feedback in maintaining a constant output voltage if input voltage and duty cycle are fixed, suggesting that output voltage should remain stable regardless of load.
- Another participant counters that input voltage is rarely fixed and that load variations can cause output voltage droop, emphasizing the role of feedback in adjusting the duty cycle to maintain output voltage.
- It is noted that the boost converter operates under the assumption of continuous conduction mode (CCM) and that real-world conditions necessitate duty cycle adjustments to stabilize output voltage.
- Participants discuss the relationship between Verror, Vout, and duty cycle, indicating that an increase in Verror should lead to a decrease in duty cycle, while a decrease in Vout would require an increase in duty cycle.
- One participant proposes the use of a zener diode for voltage stabilization, but another warns that this approach is inefficient and typically only suitable for low-power applications.
- There is a suggestion that simpler designs, such as using a 555 timer, could be employed for boost converters, but the efficiency of switching regulators is highlighted as a significant advantage.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express differing views on the necessity and effectiveness of feedback in boost converter designs, with some advocating for its importance while others propose alternative methods. The discussion remains unresolved regarding the optimal approach to voltage stabilization in boost converters.
Contextual Notes
Participants acknowledge that assumptions about fixed input voltage and ideal component behavior may not hold in practical applications, which complicates the analysis of duty cycle adjustments and feedback mechanisms.