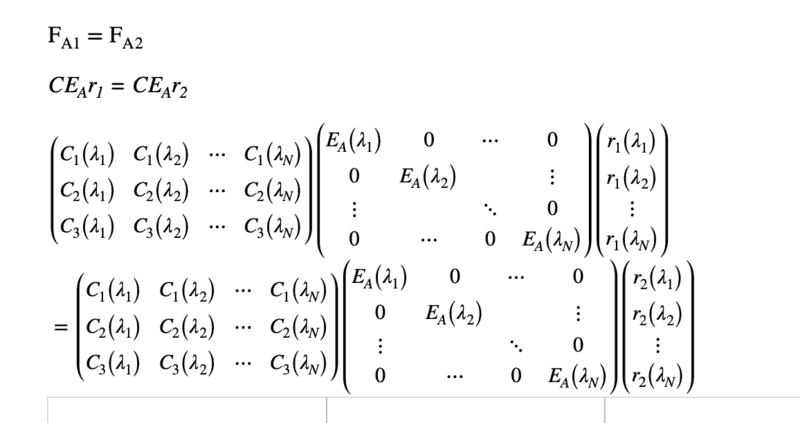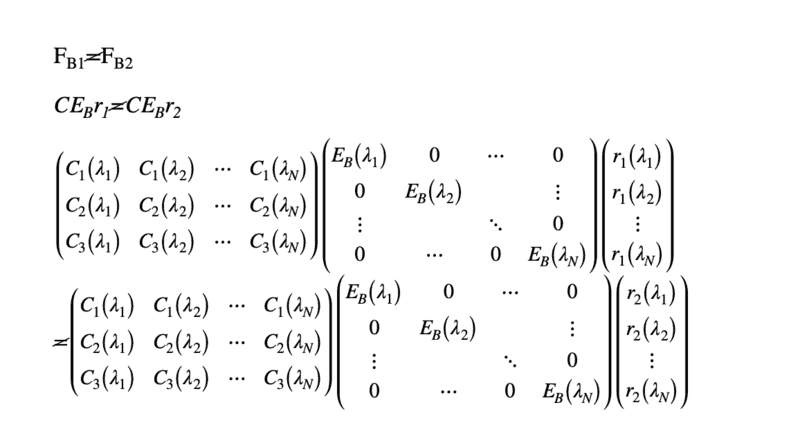SUMMARY
This discussion focuses on metamerism in color perception using vector-matrix representation. The user seeks clarification on how two objects can appear the same under illuminant spectrum A but differ under illuminant spectrum B. The importance of defining variables and functions related to color perception is emphasized for better assistance. The conversation highlights the necessity of understanding the underlying principles of color theory and the impact of different illuminants on color appearance.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of metamerism in color theory
- Familiarity with vector-matrix representation
- Knowledge of illuminant spectra, specifically illuminant A and B
- Basic principles of color perception and color mixing
NEXT STEPS
- Research the principles of metamerism in color science
- Learn about vector-matrix transformations in color representation
- Study the characteristics of different illuminants, focusing on illuminant A and B
- Explore the role of color perception in digital imaging and display technologies
USEFUL FOR
This discussion is beneficial for color scientists, graphic designers, and anyone involved in digital imaging or color calibration who seeks to understand the complexities of color perception under varying lighting conditions.