- #1
Konte
- 90
- 1
Hello everybody,
I have read some very interesting book (Molecular symmetry and Spectroscopy - Bunker and Jensen) that talk about how to find the Molecular Symmetry group (MS) of a molecule by using the concept of "feasible" operation from the Complete Nuclear Permutation Inversion (CNPI) group.
Following the explanation given by the authors, "feasible" operation is that can interconverts a numbered and equivalent equilibrium versions of the molecule (rigid or non-rigid).
Confident of this understanding, I tried and success on finding MS of some famous non-rigid molecule until I met certain hard case as of the butane molecule which have non equivalent equilibrium versions!
So, my question is :
How to define the MS group of such a non-rigid molecule that have non equivalent equilibrium versions, knowing that between theses non equivalent equilibrium versions, potential barrier is not too high and allow some interconversion between the different versions of the same molecule?
I attached here the potential energy of butane as an example of those molecule which have more than one equilibrium versions:
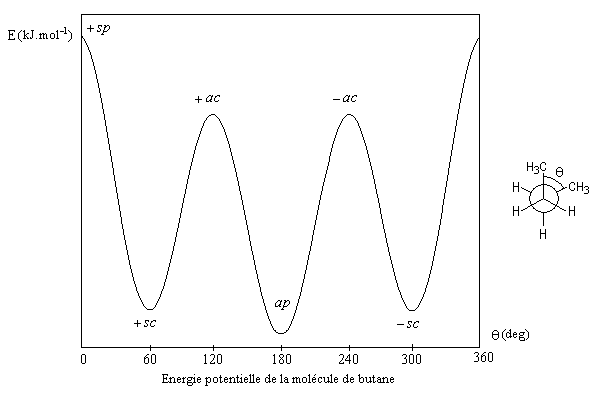
Thank you very much everybody.
Konte.
I have read some very interesting book (Molecular symmetry and Spectroscopy - Bunker and Jensen) that talk about how to find the Molecular Symmetry group (MS) of a molecule by using the concept of "feasible" operation from the Complete Nuclear Permutation Inversion (CNPI) group.
Following the explanation given by the authors, "feasible" operation is that can interconverts a numbered and equivalent equilibrium versions of the molecule (rigid or non-rigid).
Confident of this understanding, I tried and success on finding MS of some famous non-rigid molecule until I met certain hard case as of the butane molecule which have non equivalent equilibrium versions!
So, my question is :
How to define the MS group of such a non-rigid molecule that have non equivalent equilibrium versions, knowing that between theses non equivalent equilibrium versions, potential barrier is not too high and allow some interconversion between the different versions of the same molecule?
I attached here the potential energy of butane as an example of those molecule which have more than one equilibrium versions:
Thank you very much everybody.
Konte.