- #1
Spinnor
Gold Member
- 2,216
- 430
Other than Helium do Noble gases with even nuclear spin form superfluids?
Is there a simple quantum mechanical explanation why the difference below of the Melting point and Boiling point of the Noble gases is roughly the same value? A yes or no would suffice.
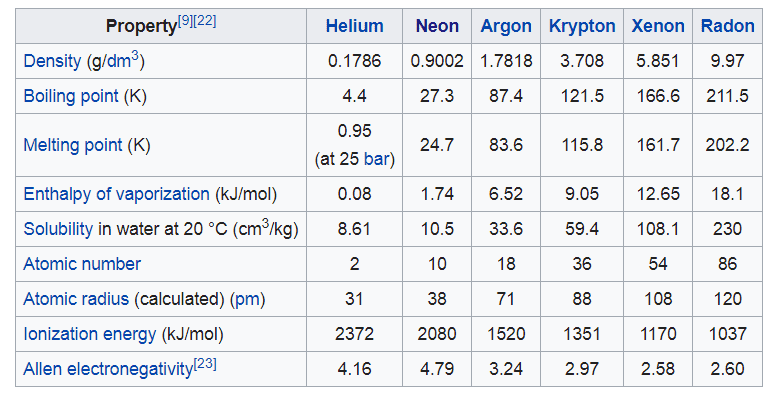
From, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Noble_gas#Physical_and_atomic_properties
Thanks!
Is there a simple quantum mechanical explanation why the difference below of the Melting point and Boiling point of the Noble gases is roughly the same value? A yes or no would suffice.
From, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Noble_gas#Physical_and_atomic_properties
Thanks!