Sonderval
- 234
- 11
Dear all,
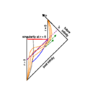
I have a question on Penrose diagrams. Consider a collapsing star that forms a black hole with a Schwarzschild radius normalized to 1. What happens in the Penrose diagram when additional matter falls in? I suspect the diagram then has to look like this :
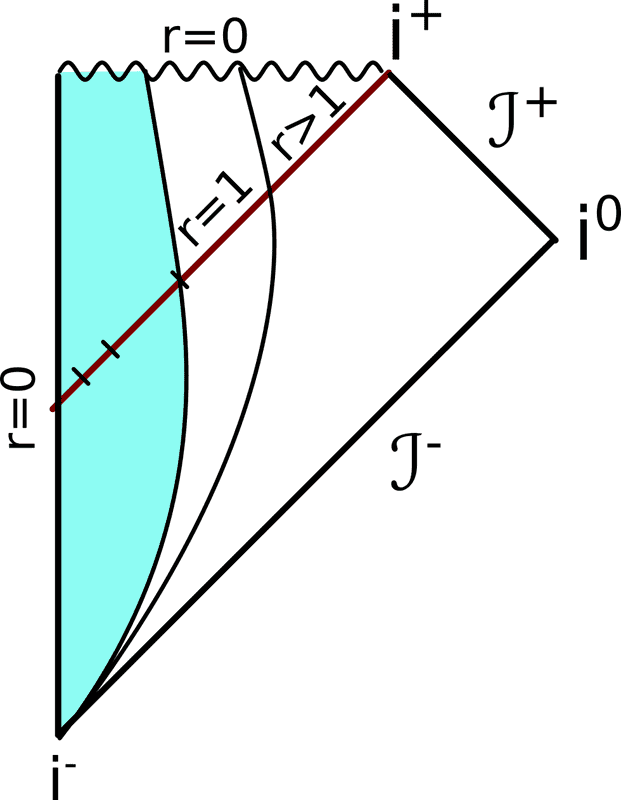
When the outer shell (second curved line) reaches the event horizon, the radius of the BH will increase (r>1). Is this diagram correct? If so, what would happen when a photon is emitted exactly at the moment the BH forms? This photon would then be frozen at the event horizon, but from the diagram it seems as if it could actually move outward to the greater event horizon (because it follows a 45-degree line). Or is this way of thinking incorrect and the diagram looks different?
The second question is related. Here is the diagram for an evaporating BH (from inspirehep)
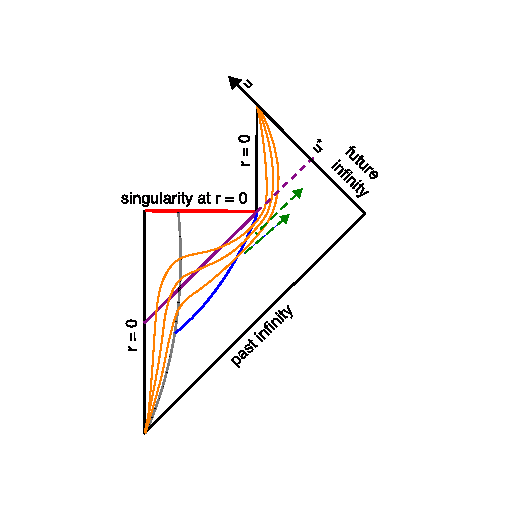
Again, I am wondering what happens to a photon trapped at the event horizon when the hole shrinks? Will it be "sucked inwards" and stay at the event horizon until the BH has evaporated completely and will then emerge from the r=0-position?
Thanks for any help,
Martin
I have a question on Penrose diagrams. Consider a collapsing star that forms a black hole with a Schwarzschild radius normalized to 1. What happens in the Penrose diagram when additional matter falls in? I suspect the diagram then has to look like this :
When the outer shell (second curved line) reaches the event horizon, the radius of the BH will increase (r>1). Is this diagram correct? If so, what would happen when a photon is emitted exactly at the moment the BH forms? This photon would then be frozen at the event horizon, but from the diagram it seems as if it could actually move outward to the greater event horizon (because it follows a 45-degree line). Or is this way of thinking incorrect and the diagram looks different?
The second question is related. Here is the diagram for an evaporating BH (from inspirehep)
Again, I am wondering what happens to a photon trapped at the event horizon when the hole shrinks? Will it be "sucked inwards" and stay at the event horizon until the BH has evaporated completely and will then emerge from the r=0-position?
Thanks for any help,
Martin