Timtam
- 40
- 0
I have a high pressure volume coupled with a low pressure volume by a pipe and valve .
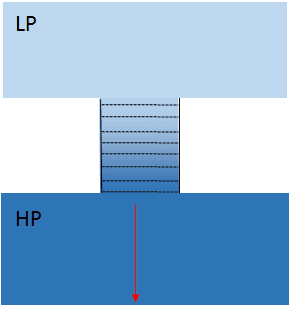
If the pipe was straight I would expect the isobars of the pressure gradient to be parallel to the pressure differences and perpendicular to the pipe , I would expect a reaction force (red arrow) on the wall directly opposite the valve acting perpendicular to the isobars (no shear component)
If the pipe was angled I am unsure how the pressure gradients isobars would look ?
Would they still be parallel between the pressure difference
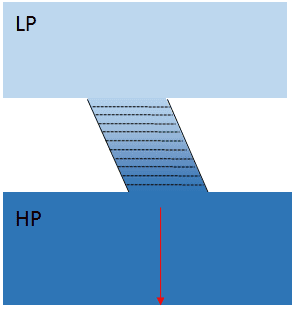
or would they still be perpendicular to the pipe ?
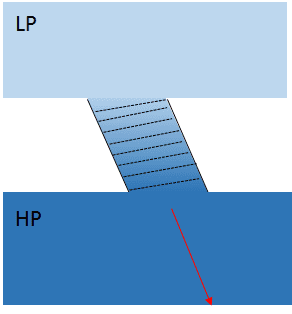
Would the angle of the pipe make a difference to where the reaction force angle on the opposite wall
If the pipe was straight I would expect the isobars of the pressure gradient to be parallel to the pressure differences and perpendicular to the pipe , I would expect a reaction force (red arrow) on the wall directly opposite the valve acting perpendicular to the isobars (no shear component)
If the pipe was angled I am unsure how the pressure gradients isobars would look ?
Would they still be parallel between the pressure difference
or would they still be perpendicular to the pipe ?
Would the angle of the pipe make a difference to where the reaction force angle on the opposite wall